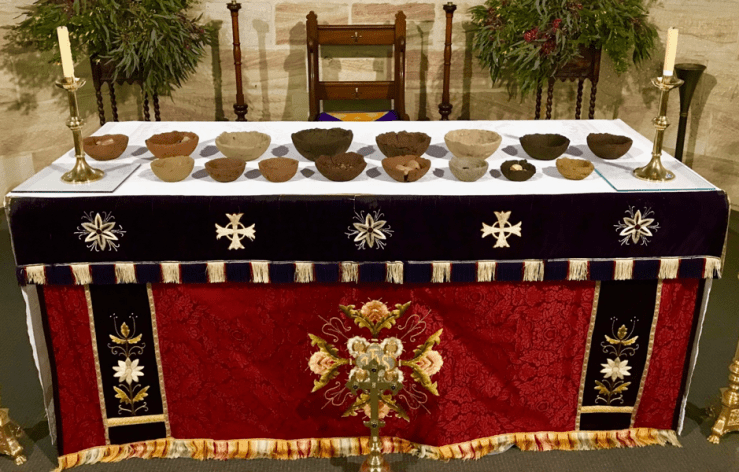
The LORD said to Moses and Aaron in the land of Egypt, “This month shall be for you the beginning of months. It shall be the first month of the year for you. Tell all the congregation of Israel that on the tenth day of this month every man shall take a lamb according to their fathers’ houses, a lamb for a household. And if the household is too small for a lamb, then he and his nearest neighbor shall take according to the number of persons; according to what each can eat you shall make your count for the lamb. Your lamb shall be without blemish, a male a year old. You may take it from the sheep or from the goats, and you shall keep it until the fourteenth day of this month, when the whole assembly of the congregation of Israel shall kill their lambs at twilight.
“Then they shall take some of the blood and put it on the two doorposts and the lintel of the houses in which they eat it. They shall eat the flesh that night, roasted on the fire; with unleavened bread and bitter herbs they shall eat it. Do not eat any of it raw or boiled in water, but roasted, its head with its legs and its inner parts. And you shall let none of it remain until the morning; anything that remains until the morning you shall burn. In this manner you shall eat it: with your belt fastened, your sandals on your feet, and your staff in your hand. And you shall eat it in haste. It is the LORD’s Passover. For I will pass through the land of Egypt that night, and I will strike all the firstborn in the land of Egypt, both man and beast; and on all the gods of Egypt I will execute judgments: I am the LORD. The blood shall be a sign for you, on the houses where you are. And when I see the blood, I will pass over you, and no plague will befall you to destroy you, when I strike the land of Egypt.
“This day shall be for you a memorial day, and you shall keep it as a feast to the LORD; throughout your generations, as a statute forever, you shall keep it as a feast.”
—Exodus 12:1–14
+++
SONG: “Passover Song” by IAMSON (Orlando Palmer), on Bread for the Journey by Urban Doxology (2016) and iAmSon (2017)
Passover is a major Jewish holiday celebrated every spring, marking God’s deliverance of the people of Israel out of Egyptian bondage. Exodus 12 tells the story of how in Egypt God sent death as a means of judgment against oppressors but “passed over” the houses of the faithful who, following God’s instructions, smeared their doorposts with the blood of a lamb.
Christians interpret this event as a prefiguration of the death of Jesus, the lamb of God, whose blood saves from death those who choose to place themselves under it, liberating us from our slavery to sin. Driving home the connection, all four Gospel writers mention that Jesus was killed during the feast of Passover. His blood smeared the wooden posts of the cross.
+++
Father Sieger Köder was born in Wasseralfingen in Swabia in southwestern Germany in 1925. From 1947 to 1951 he attended the State Academy of Fine Arts Stuttgart, where he trained as a silversmith and a painter. While establishing his art practice, he also worked as an art teacher at a secondary school in Aalen for just over a decade. Increasingly he felt a pull into Christian ministry, so from 1965 to 1970 he studied theology in Tübingen, becoming ordained in the Catholic Church a year later. He served as a parish priest in Hohenberg and Rosenberg from 1975 to 1995, combining that vocation with his work as an artist. He continued his art making well into retirement, dying in 2015 at age ninety. His religious paintings can be found all over Germany and in other parts of Europe.
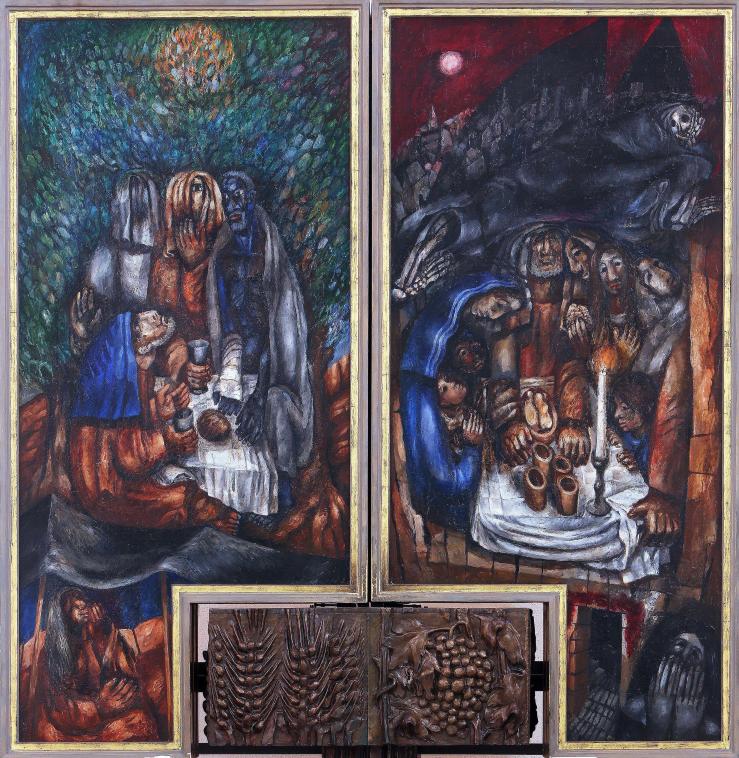
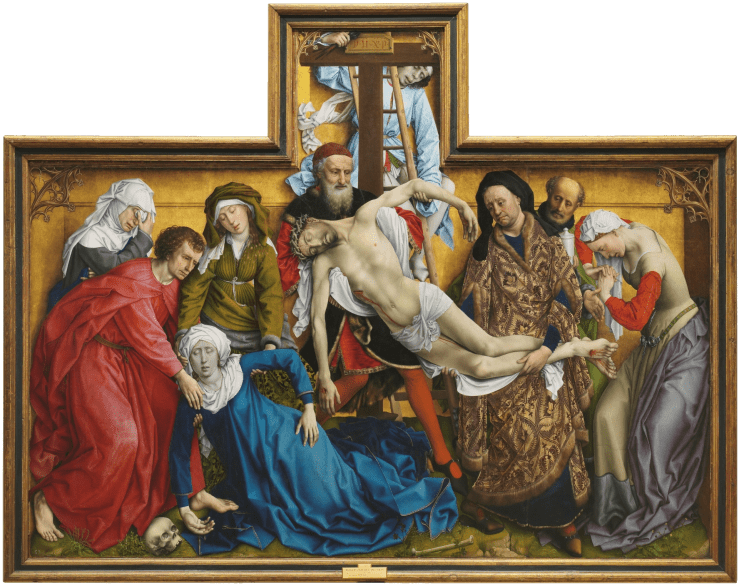
The artwork above is the closed view of the high altarpiece Köder made for the parish church in his hometown, Saint Stephen’s (Sankt Stephanus).

The outer left panel shows the Hospitality of Abraham (Genesis 18:1–21)—that is, Abraham’s entertaining three men who turn out to be a theophany, an appearance of God in a human body (or in this case, three human bodies). I’m guessing that the man on the left, who is veiled, represents God the Father; the man in the middle, who’s holding the cup, is God the Son; and the man on the right, who appears to have a broken arm and to be naked except for a blanket draped over him, is God the Spirit—though he is likely also meant to show how God often comes to us in the guise of the poor, the hungry, the unsheltered (Matthew 25:31–46). Above the heads of this trinity, glowing through the oak leaves, is a fiery orb reminiscent of the burning bush from which God would call Moses a few centuries later. At the bottom of the painting Abraham’s wife Sarah laughs from inside her tent, having eavesdropped on the visitors’ news that she, a nonagenarian, will conceive a child. The lineage of that child, Isaac, would produce Jesus.
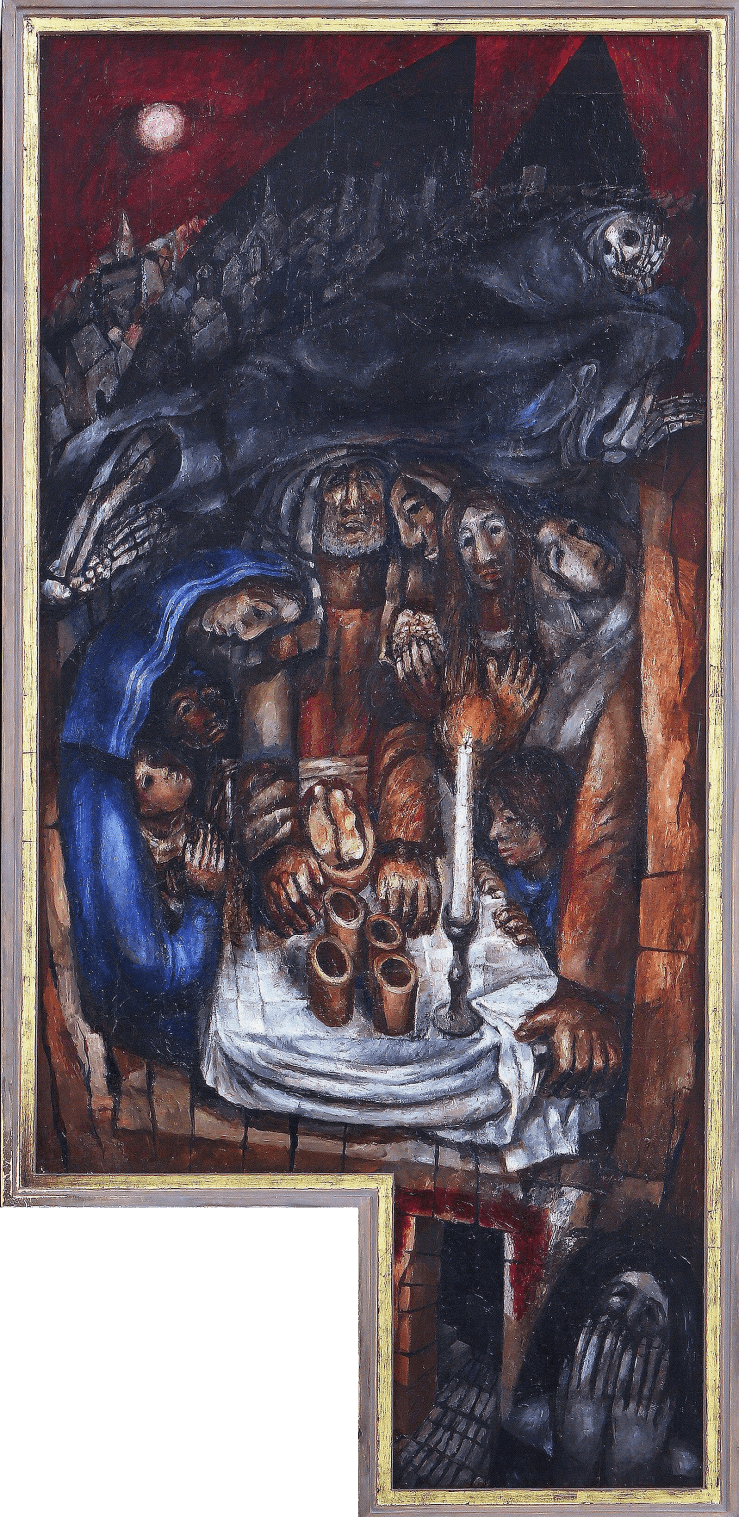
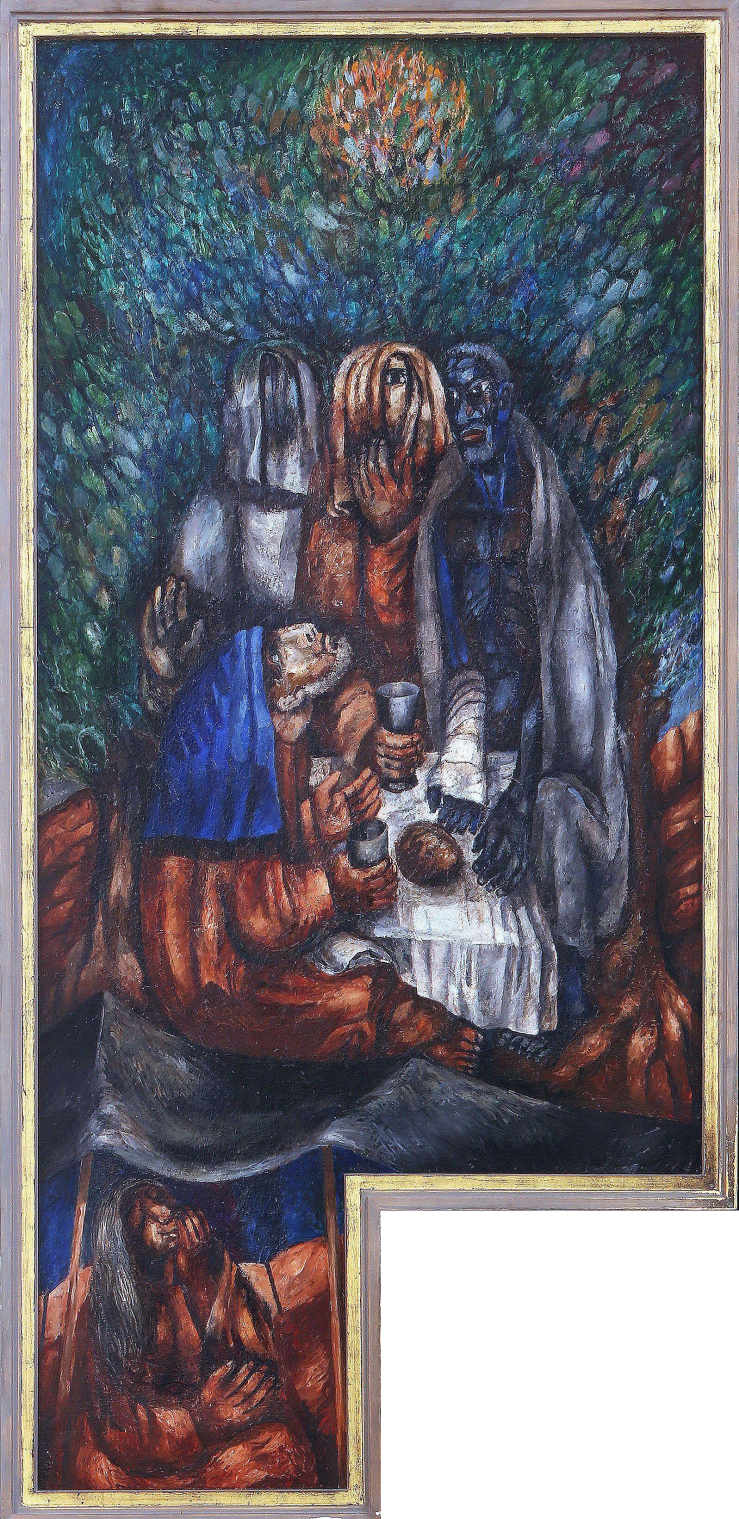
The outer right panel, based on Sunday’s lectionary reading, shows the first Passover. Israelite families huddle around a meal of roast lamb, unleavened bread, and bitter herbs as a cloaked, skeletal presence passes by overhead. One of the adults tries to steady the rattling table with his hand while a mother protects two of her children, hugging them tightly to herself. Though afraid, they are in no danger, as their doorway is covered in the blood of the lamb whose flesh they eat.

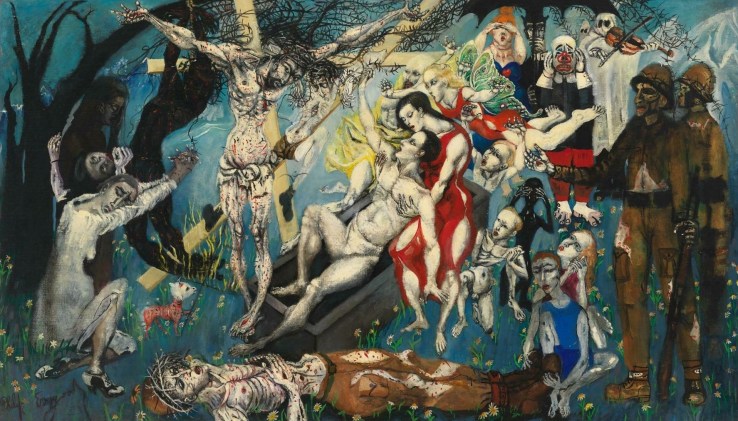
When opened, the triptych reveals three Resurrection-themed panels. The inner left panel shows one of my favorite biblical episodes, which I call “Breakfast on the Shore”: Jesus’s resurrection appearance to Peter at dawn on the Sea of Galilee (John 21). Following Jesus’s instruction in Jerusalem (Matthew 28:7, 10), Peter had returned home with some of the other disciples and, not knowing what to do, took back up his fishing nets. He and six others are on the lake when a man calls out from the shore, “Children, do you have any fish?” They don’t. The man tells them to cast in their nets once more, and when they do, up comes a humongous catch. After which Peter exclaims, “It is the Lord!” Ever the impulsive one, he throws himself into the sea and pushes his way through the water to greet Jesus. They chargrill some of the fish and sit down to eat.

The scene is one of reconciliation. Peter had denied he knew Jesus three times the night of Jesus’s arrest, abandoning him in his time of need, and now, after breakfast, Jesus gives Peter three chances to reaffirm his love for him, asking him thrice, “Simon, son of John, do you love me?” The foregrounding of the hot coals in Köder’s painting is perhaps a subtle nod to the recent failure of Peter’s, as earlier in his Gospel John mentions that, in the courtyard of the high priest where Jesus was being tried, Peter warmed himself at a charcoal fire alongside Jesus’s captors (John 18:18). There’s also a hand coming up out of the water that I’m guessing references the earlier episode of Peter’s walking on water and then, when doubt in Jesus’s power set in, sinking, only to be saved by Jesus’s outstretched hand (Matthew 14:22–33). But Jesus forgives Peter’s weaknesses and disloyalty, restoring him to fellowship. He invites Peter to come and feast. The sun at the top indicates that it’s the dawn of a new era.
The bright-red morning sun also appears on the inner right panel, which shows another very personal encounter between the risen Christ and a disciple: Mary Magdalene at the empty tomb. In Köder’s visual retelling, Mary wades through a sea of poppies—a red flower symbolic of sacrifice—her hand shielding her eyes from the brilliance of Jesus’s resurrection body. He who she initially thought to be the cemetery gardener is in fact her dear friend and Lord.

Look closely at some of the grave markers, and you’ll notice that they carry the names and/or dates of wars: “1914–1918,” “1939–1945,” “Vietnam,” “Biafra” (a reference to the Nigerian Civil War). The latter two were still raging on when Köder painted this. The artist was actually a prisoner of war during World War II, and underneath the cross representing that war in the painting is a bullet-blasted soldier’s helmet. I take these graves to imply that Jesus’s resurrection put death to death.
I’m not sure what the Hebrew grave inscriptions say—anyone know?
Update, 9/30/21: Dr. Franz Posset, a former student of the artist’s, emailed me today with transcriptions and translations of the Hebrew tombstone inscriptions:
- האדם – Adam, The Man (lower right corner, next to Mary’s elbow)
- חוה – Eve, The Woman (in the shadows at the right, behind the “Vietnam” tombstone)
- החכם – The Wise (to the right of Mary’s raised hand)
- כסילה – The Fool (to the left of Mary’s raised hand)

The central panel of the altarpiece portrays the Supper at Emmaus as a sort of Transfiguration à la Mount Tabor, an unveiling of Christ’s glory. Luke tells us that after the resurrection Jesus appeared to Cleopas and another unnamed disciple, who were on their way home from Jerusalem; their hearts “burned within them” as he spoke about the scriptures, but their eyes weren’t opened to his true identity until he blessed and broke the bread at mealtime. In Köder’s painting, Jesus’s form is barely discernible through the red glow—he’s a pillar of light, really. Artists have always struggled to give an impression of what Jesus’s resurrection body might have looked like: it was a flesh-and-bone body, for sure, but a glorified one, not always immediately recognizable, and it seems as though he was able to walk through walls and disappear. Köder bathes him in the color of blood—of his passion, and of life. Köder’s nonrepresentational approach emphasizes the otherness aspect of the newly risen Christ and the marvel the two Emmaus disciples must have felt upon realizing who they were dining with.
Jesus appears between Moses, who holds a basket of manna (Exodus 16), and Elijah, who cradles a raven with a morsel of bread in its beak, a reference to his being fed miraculously by God in the wilderness (1 Kings 17:1–7). The figure to the right of Elijah may be Paul (Saul) fallen off his horse on the road to Damascus.
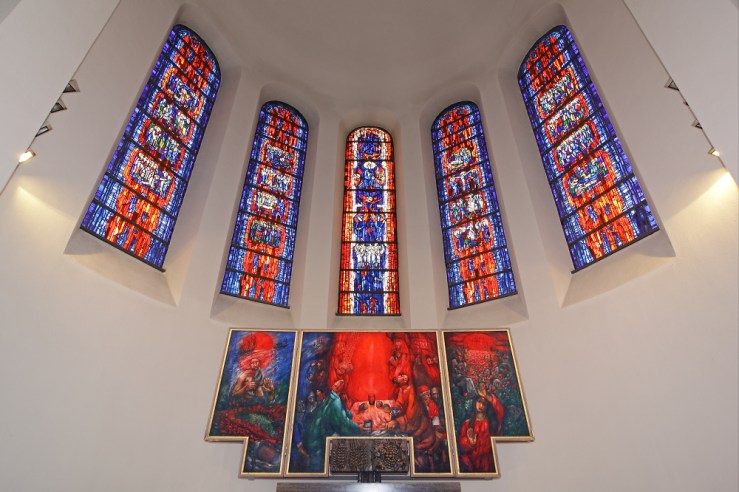

At Saint Stephen’s the Eucharist is celebrated regularly before this altarpiece. (The metalwork tabernacle below, decorated with stalks of grain and clusters of grapes, is where the eucharistic elements are stored.) Köder reminds partakers that they are covered (pardoned) by Jesus’s blood, that Christ is present in the meal, that he nourishes and sustains his people with his very self. Death has passed over us because it struck the firstborn of all creation, who bore the curse on our behalf. However, death could not keep him down, and on the third day he rose again, appearing to many, the firstborn of new creation. “Mary,” he called out to one of his closest followers outside his tomb, speaking her name in a familiar tone, sparking recognition and joy. “Come and have breakfast,” he called out to Peter. To the Emmaus disciples he illuminated the scriptures and finally revealed himself around a table. Christ invites us into fellowship with him, through his blood.
P.S. It appears there is yet a third configuration of the altarpiece, as indicated by this photo, which includes a Madonna and Child, the Tower of Babel, and I can’t make out the left two panels.
This post belongs to the weekly series Artful Devotion. If you can’t view the music player in your email or RSS reader, try opening the post in your browser.
To view all the Revised Common Lectionary scripture readings for Proper 18, cycle A, click here.