HOLY WEEK TRADITION: Antigua, Guatemala, is renowned for its annual Good Friday observance, which involves the laying out of alfombras (carpets) of multicolored sawdust through the city’s cobblestone streets, hundreds of feet long. On Maundy Thursday, the city closes so that families and businesses can spend the day constructing the carpets, applying the sawdust to planned designs using stencils and strainers and adding pine needles, flowers, fruits, and other natural materials as well.
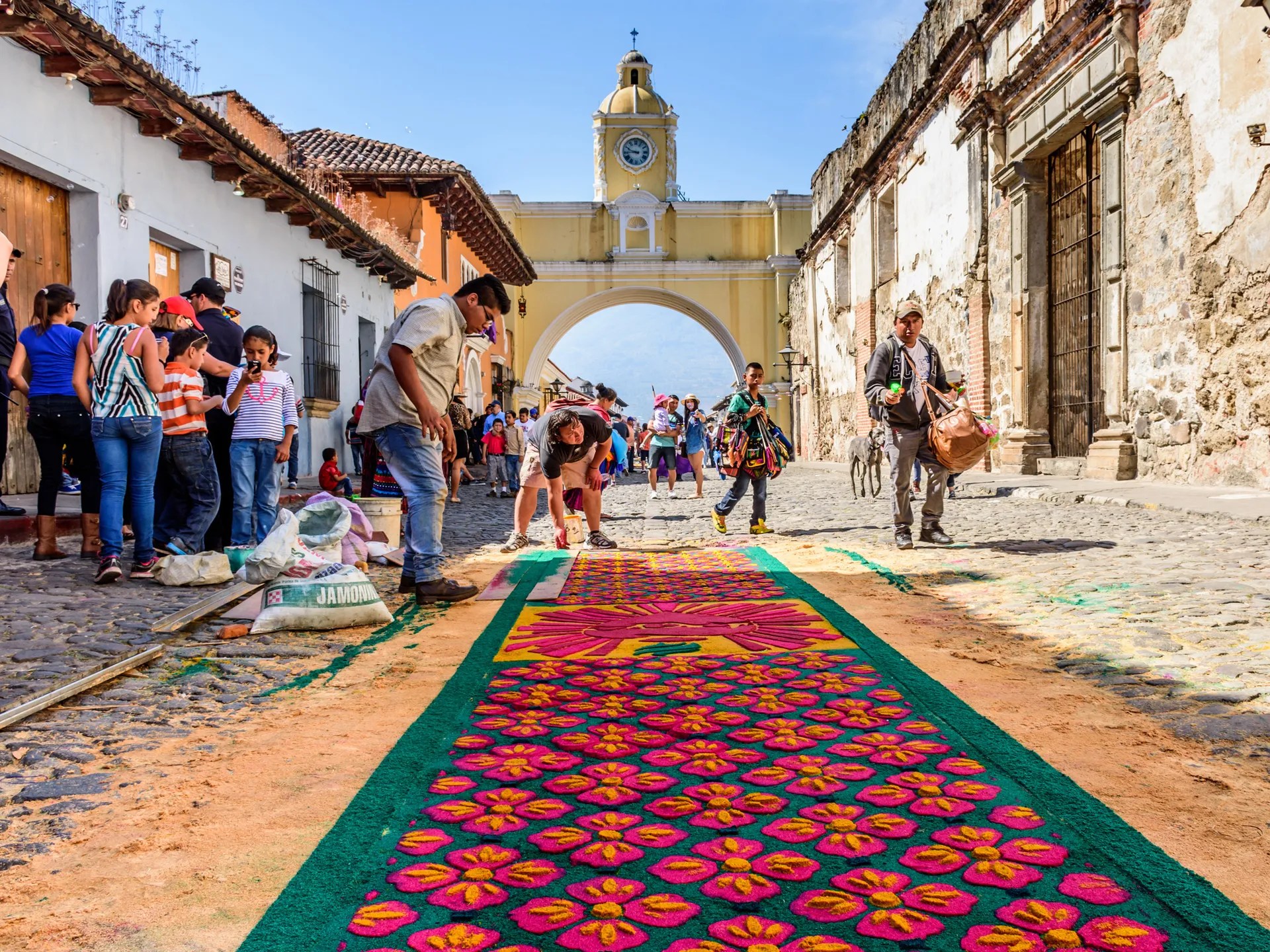

At 4 a.m. on Good Friday, the processions begin, with people carrying floats that bear statues of Christ carrying his cross, followed by marching bands playing solemn music. (This is a remembrance of Jesus’s walk to Calvary.) As their feet pass over the alfombras, the dust scatters. Locals and visitors gather along the streets dressed in black for mourning, and at 11 p.m. a figure of Jesus is laid to rest in the church.
Here are two resources for exploring this tradition further:
>> ARTICLE: “Exploring Guatemala’s Vibrant Easter Tradition” by Meredith Carey
>> VIDEO: “Alfombras de Semana Santa en Guatemala,” dir. Federica Dominguez: This short film (in Spanish, with English subtitles) interviews Rolando Ortiz, an alfombrero who is also a shoemaker. He explains that the carpets hark back to Jesus’s triumphal entry into Jerusalem, when the crowds strewed his path with palm branches (giving him the red carpet treatment, so to speak). Even though the alfombras last only a brief time, locals spare no expense in bringing them to fruition each year—“for Jesus,” Ortiz says. “It is an act of gratitude above all.” An offering of beauty and praise.
+++
NEW ALBUM: As Foretold, Part 3 by Poor Bishop Hooper: Released today, this is the final album in a trilogy based on the prophetic fulfillment passages in the Gospel of Matthew. It centers on Jesus’s passion and concludes with a resurrection epilogue. As with all their music, the duo graciously offers it for free download from their website.
+++
SONGS performed by Emorja Roberson: Emorja Roberson [previously] is a singer, gospel choir conductor, and assistant professor of music and African American studies at Oxford College of Emory University in Georgia. I enjoy following his YouTube channel. Here are two songs that are especially fitting for Holy Week.
>> “I Know It Was the Blood”: Roberson sings three verses of this beloved African American spiritual: the title verse, “They whipped him all night long,” and “He never said a mumblin’ word.” The song is more typically sung in a major key, and its full lyrics span Christ’s passion, resurrection, ascension, and second coming. But Roberson slows down the tempo and sings in a minor key, homing in on the sorrow of Good Friday.
>> “He Decided to Die” by Margaret Pleasant Douroux: Roberson, on keys, sings a gospel classic with friends Marcus Morton and Cameron Scott, a song that emphasizes Christ’s resoluteness on the cross, his endurance for love.
+++
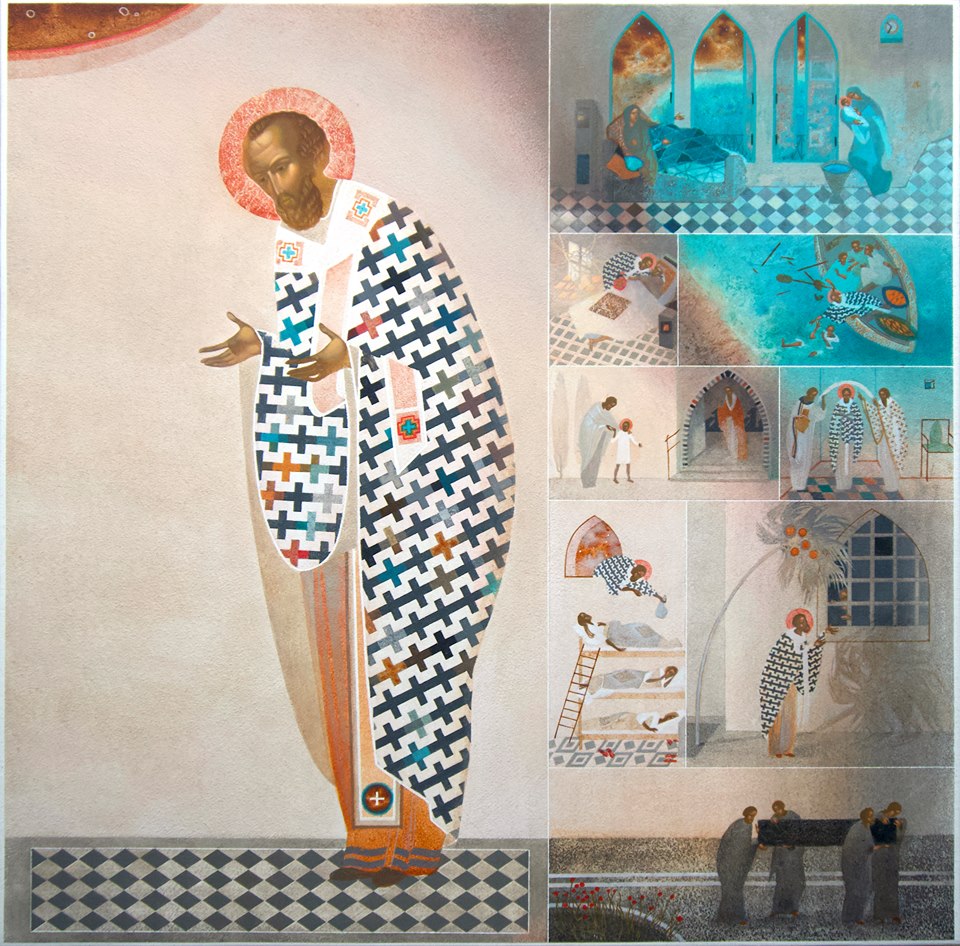
VISUAL COMMENTARIES: “After the Order of Melchizedek” by Victoria Emily Jones: My latest contribution to the Visual Commentary on Scripture, a project based out of King’s College London, was published earlier this month. Tasked with choosing and commenting on three artworks that dialogue with Hebrews 7–8, I landed on a “You Are a Priest Forever” icon from Russia (very strange!), an Antwerp Mannerist triptych that centers the Last Supper, and (my favorite) a wall painting of Christ the Grapevine from a Romanian church. I was interested to explore the idea of how Jesus, in giving his body and blood, is both the offerer and the offered, both priest and sacrifice.
+++
POEM: “The Death of Christ” by Emperor Kangxi: Emperor Kangxi (1654–1722) ruled in China for sixty-one years during the Qing Dynasty. In 1692 he issued the Edict of Toleration, which barred attacks on churches and legalized the practice of Christianity among Chinese people. Curious about and respectful of other faiths, he penned this short poem on the Crucifixion using the classical qi-yen-she form.
+++
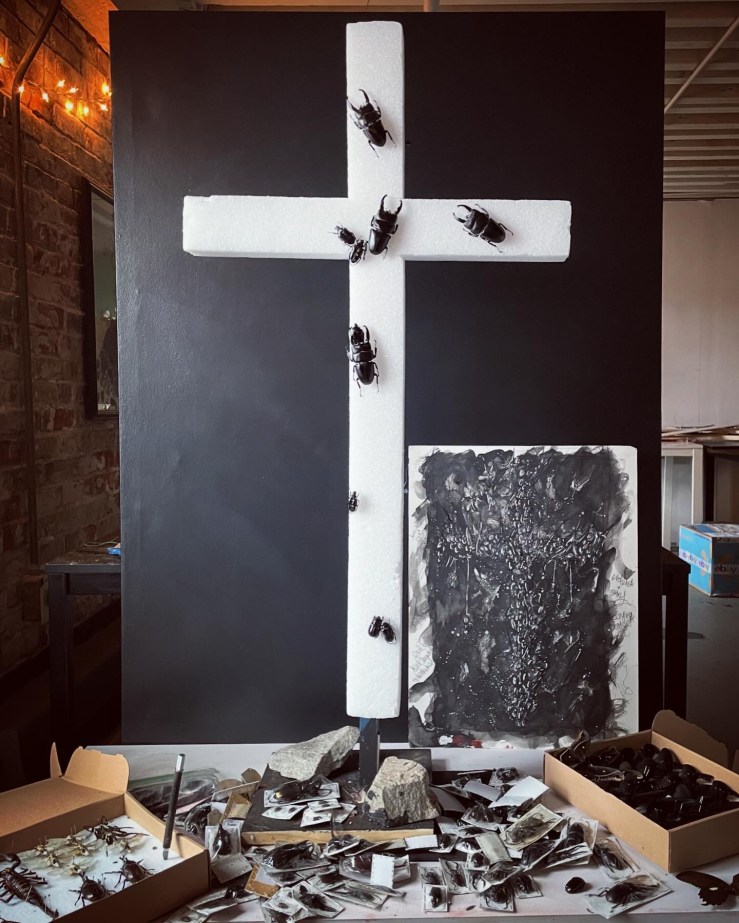
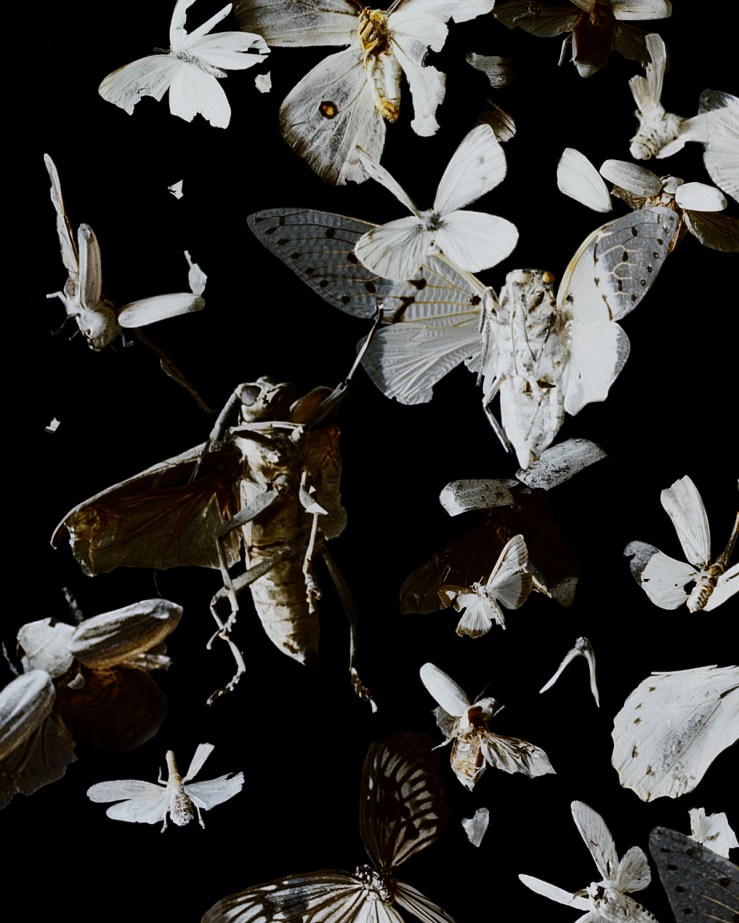
EXHIBITION: Tara Sellios: Ask Now the Beasts, Fitchburg Art Museum, January 18, 2025–January 18, 2026: Tara Sellios is a multidisciplinary artist from South Boston working mainly in large-format photography. Delighting in detail and complex symbolism, she often uses insects, dried fauna, bone, and other organic matter to create elaborate still lifes that she then photographs under dramatic lighting. She is inspired by art historical representations of the end of the world, especially the bizarre paintings of Hieronymus Bosch and Albrecht Dürer’s Apocalypse woodcuts, and by seventeenth-century Dutch vanitas paintings.
The photographs in her current solo show, Ask Now the Beasts at Fitchburg Art Museum in Massachusetts, are “contemporary allegories of suffering and transcendence.” The exhibition’s title comes from Job 12:7.
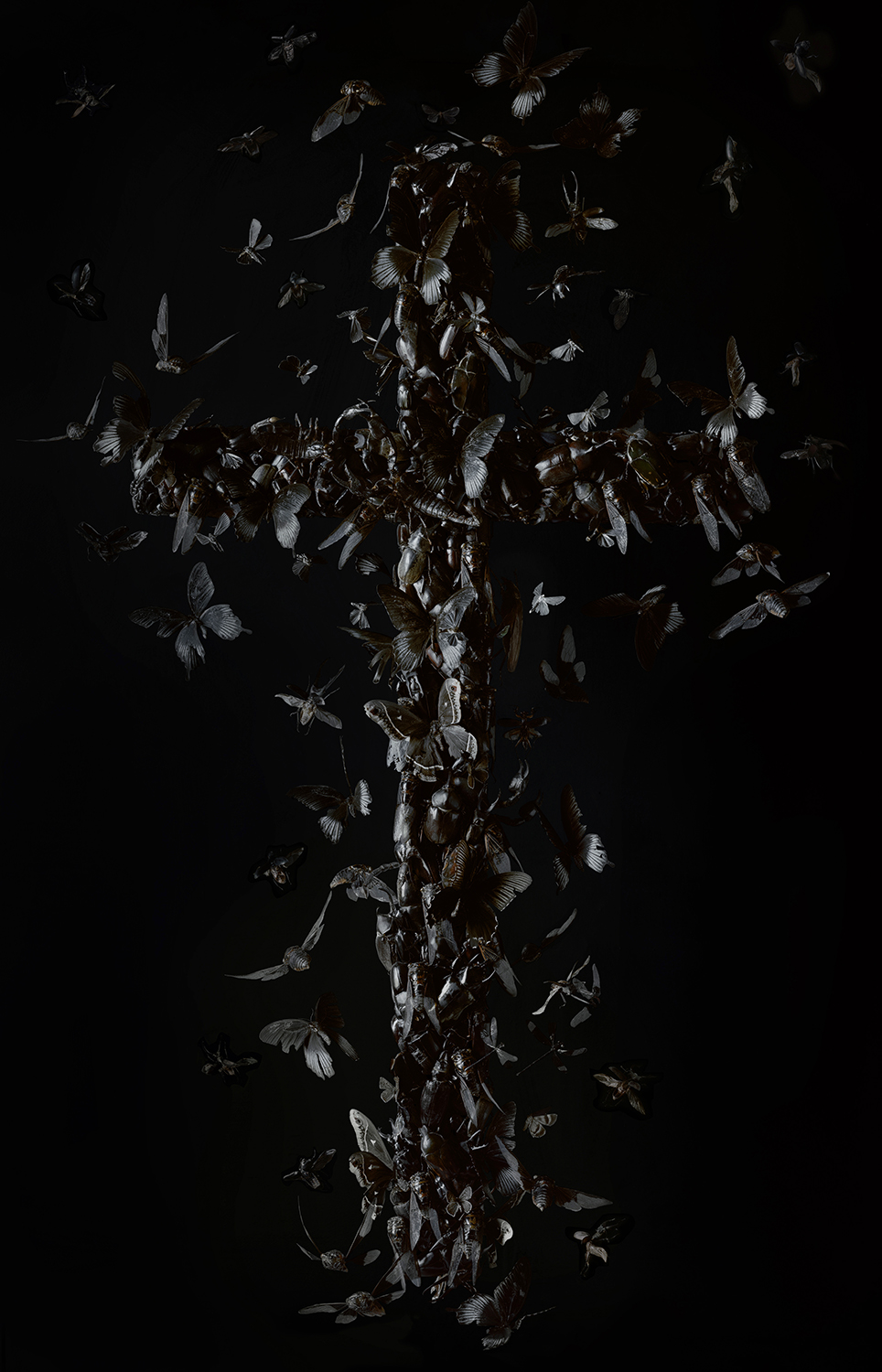
Two of the works on display are a pair of crosses: Umbra (Latin for “darkness” or “shadow”) and Dilucesco (“to begin to grow light, to dawn”), which together suggest a movement from death to resurrection. Constructed with a throng of black beetles and other black insects, the Umbra cross evokes the detail from the Synoptic Gospels’ Crucifixion accounts that at noon, “darkness came over the whole land until three in the afternoon, while the sun’s light failed” (Luke 23:44–45; cf. Matt. 27:45; Mark 15:33). Dilucesco, on the other hand, shows the cross seemingly exploding into light, as white moths and other winged insects break out of their cruciform shape. View these two photographic artworks, plus a few process photos and sketches the artist sent me, below. See, too, www.tarasellios.com.















