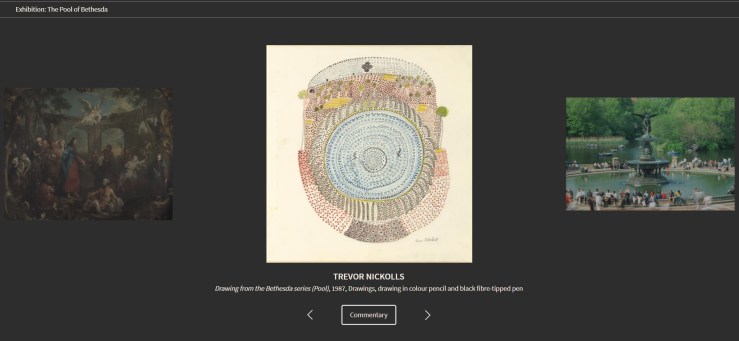
VISUAL COMMENTARIES: “The Pool of Bethesda” by Naomi Billingsley: In a recent contribution to the online Visual Commentary on Scripture [previously], Naomi Billingsley has compiled and written about three artworks based on John 5:1–18, a story in which Jesus heals a paralyzed man at a reservoir in Jerusalem. A source of hydration, cleansing, and tranquility, the pool of Bethesda, Billingsley says, is a symbol that transcends individual religious traditions.
She discusses William Hogarth’s painting of the subject for a hospital, showing sick patients receiving care; a “Dreamtime” drawing from Aboriginal Australian artist Trevor Nickolls’s Bethesda series, created during his recovery from a major car accident; and The Angel of the Waters fountain in Bethesda Terrace in Manhattan’s Central Park, designed by Emma Stebbins in 1842 to celebrate an aqueduct that brought clean water to New York City and improved public health (and which you may recognize as the site where John the Baptist baptizes disciples in the opening sequence of the movie Godspell).
+++
ARGENTINE TANGO HYMN: “Tenemos Esperanza” (We Have Hope): This hymn text was written in 1979 by Federico Pagura (1923–2016), a Methodist bishop and human rights champion from Argentina, and set to tango music by Homero Perera (1939–2019) of Uruguay. Argentinian pastor Federico “Fede” Apecena, who lives in Georgia in the US, recently introduced the song to his friend Josh Davis, who heads the multicultural worship ministry Proskuneo, and the two banged out this awesome video performance. “The song is a record of all that Jesus came to do and to be,” Apecena explains at the end of the video. [HT: Global Christian Worship]
+++
OBITUARY: Ernesto Cardenal (1925–2020), poet and priest who mixed religion and politics in his commitment to social justice in Nicaragua, dies at 95: A Catholic priest, poet, and political revolutionary from Nicaragua, Ernesto Cardenal was a controversial figure. He supported the Sandinista insurrection against the dictatorial Somoza regime in the seventies and, when the Sandinista government (which claimed to integrate Marxist and Christian ideals) came to power, served as its minister of culture from 1979 to 1987. He viewed this post as an extension of his priestly office and, refusing to quit it at Pope John Paul II’s behest, was forthwith suspended from the priesthood in 1984. (Pope Francis absolved him of canonical censure in February 2019, permitting him to administer the sacraments once again.)
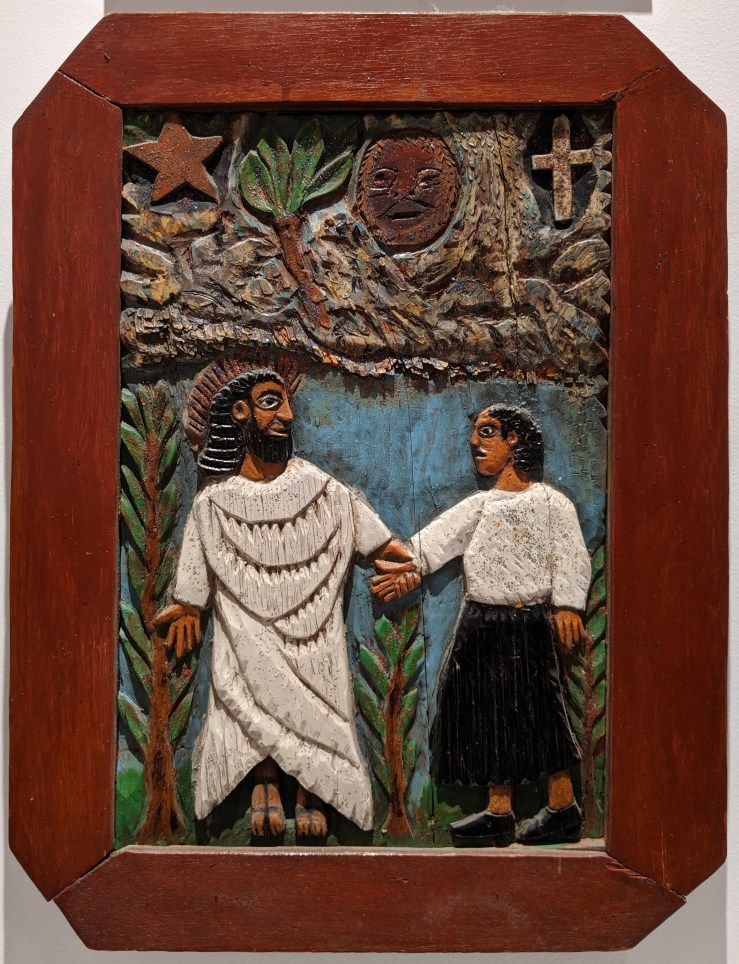
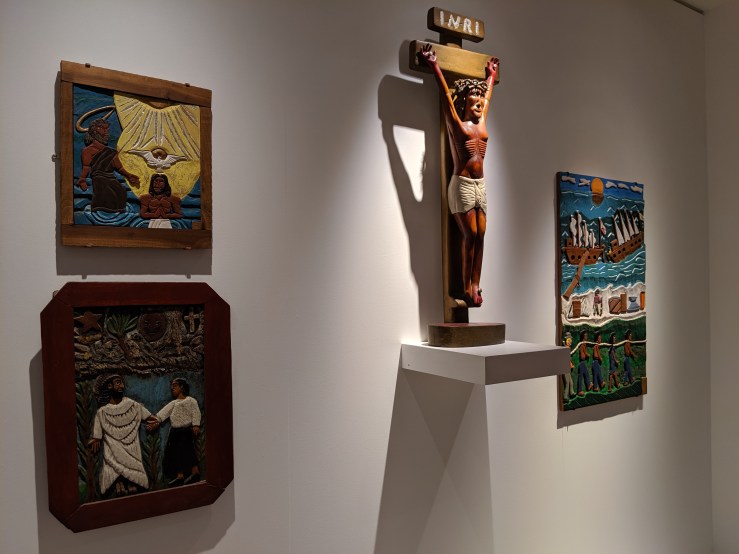
Cardenal’s most enduring achievement was his 1966 founding of a religious community among the peasant farmers and fishermen of the Solentiname archipelago in Lake Nicaragua. He saw to the construction of a small wooden church, where he led collaborative Masses: instead of giving a homily on the week’s assigned Gospel reading, he opened up dialogues about it with his parishioners, relishing their insights. Transcripts of these conversations were published in four volumes as El Evangelio en Solentiname (The Gospel in Solentiname) between 1975 and 1977, with English translations appearing in 1976–82—a classic work of liberation theology.
Besides cultivating the islanders’ interest in the Bible, Cardenal also took notice of their creative talents. He brought in artists to lead workshops, which led to the development of a primitivist art school that achieved international recognition for its paintings, many of them depicting Jesus’s birth, ministry, and passion taking place in Solentiname, in and around the familiar thatched-roof buildings, blue waters, and lush vegetation. In 1984 Orbis Books editors Philip and Sally Scharper combined several such images with a heavily abridged version of The Gospel in Solentiname and published it as The Gospel in Art by the Peasants of Solentiname, a slim, full-color hardcover that I highly recommend.

Cardenal is also known as a poet. I’ve read only one volume of his poetry, in English translation: Apocalypse: And Other Poems (New Directions, 1977). I didn’t connect well with a lot of it, but it does have a few gems, like “Prayer for Marilyn Monroe,” “The Cosmos Is His Sanctuary (Psalm 150),” and “Behind the Monastery,” reprinted here in full:
Behind the monastery, down the road,
there is a cemetery of worn-out things
where lie smashed china, rusty metal,
cracked pipes and twisted bits of wire,
empty cigarette packs, sawdust,
corrugated iron, old plastic, tires beyond repair:
all waiting for the Resurrection, like ourselves.(translated from the Spanish by Robert Pring-Mill)
+++
LECTURE: “On Beauty” by Natalie Carnes: “Beauty has been leveraged in ways that wound us, with legacies of misogyny, class hatred, and racial injustice,” says Dr. Natalie Carnes, associate professor of theology at Baylor University. “And yet I want to suggest that beauty tends those same wounds, and can be found in those same wounds, for beauty is a name for God.”
In this half-hour talk given November 1, 2017, at Dallas Theological Seminary as part of school’s Arts Week, Carnes examines the paradox, expressed in the church’s art and theology across history, that God is both beautiful and not beautiful. In his suffering, Carnes says—his entering the ravaged and scarred places of our humanity—God does not renounce his beauty but reveals it.
The divine presence in grotesque suffering is not a departure from the divine life but characteristic of it. And that movement into the grotesque is not antagonistic to beauty but the revelation of it. God’s faithfulness goes by way of intimacy with not-God, and beauty by way of the grotesque. The beauty that rejects suffering is false, and the one who follows the call of beauty faithfully will find herself in the scarred places of the world. Beauty, after all, is a name for God, and God does not abandon divinity in identifying with the suffering and afflicted but expresses through such identification the very marker of divine life.
This is not to say that suffering, affliction, or poverty is beautiful. Beauty is distinct from the mode of its arriving. Poverty and suffering can be important sites of beauty, even as they are not themselves beautiful, because they mediate the beauty of the God who is charity. . . .
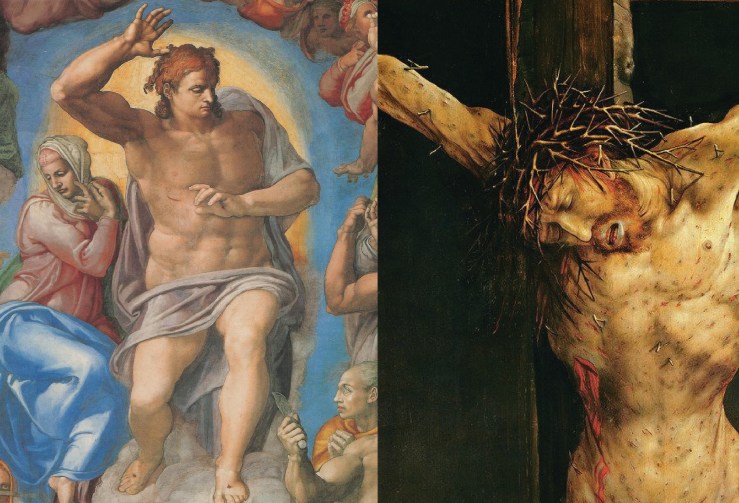
Natalie Carnes is the author of Beauty: A Theological Engagement with Gregory of Nyssa, Image and Presence: A Christological Reflection on Iconoclasm and Iconophilia, and (forthcoming) Motherhood: A Confession.
+++
PLAYLIST: “Spiritual Cosmonaut,” compiled by Latifah Alattas: Last month singer-songwriter and music producer Latifah Alattas [previously] curated a short Spotify playlist of “Spiritual songs that stir my soul. Melodies that tap into mystery. Sounds that open me up to the wonder and peace of God.” It’s great!
Alattas is the frontwoman of the band Page CXVI [previously], which has just returned from a six-year hiatus. I’m so moved by their recently released rendition of “Great Is Thy Faithfulness,” with piano, synthesizer, and pedal steel guitar. Alattas has made the song more communal, subbing out all first-person singular pronouns for first-person plural, even rewording whole lines, like the last two of the chorus, which become “Amidst the pain of this world you grieve with us—unfailing faithfulness, dwelling so near.” Or the final line of the final verse, which she changed from “Blessings all mine, with ten thousand beside!” to “Blessings for all, Christ within us resides.”
People who are attached to singing the song a certain way might object to such lyrical revisions, but I see them, along with the creative musical liberties she takes, as helping to bring out the themes that are already there. Alattas helped me to hear this classic hymn with new ears.
+++
FILM: The Two Popes (2019), dir. Fernando Meirelles: I recently watched this Oscar-nominated biographical drama and enjoyed it more than I thought I would! I wasn’t expecting the respect it gives to its subjects and to Christianity. Its title refers to the fact that, for the first time in six hundred years, the Roman Catholic Church has one reigning pope and one retired pope, the “pope emeritus.” (When Benedict announced his resignation in 2013, it shocked the world, as it’s expected that, if chosen, you serve in that role until death.)
The movie is primarily about the relationship between the traditionalist Pope Benedict XVI (born Joseph Ratzinger) and the progressive Pope Francis (born Jorge Bergoglio), which starts out antagonistically but buds into a friendship of sorts. It’s dialogue-heavy (it was adapted from a stage play), but in the most interesting way, as the two engage in “a series of philosophical and dogmatic discussions and disagreements about the nature of faith and forgiveness, and the direction of a church struggling to maintain relevance in the modern world” [source].
But it’s not just about the church’s struggle or the burdens of high office; it’s also about personal faith as a struggle—how to discern one’s calling in life, how to hear God’s voice and deal with his silence, and how to forgive oneself for one’s own tragic silences (in Benedict’s case, regarding the sex abuse perpetrated by clergy; in Francis’s, regarding the Dirty War in his home country of Argentina in the late seventies and early eighties, while he was serving as priest).
Francis’s backstory, of which I knew nothing beforehand, is told in flashbacks. (The fiancée is fictional, though the real Francis has admitted to having romantic crushes as a teenager and even as a seminarian.) The portrayal of both men, by Anthony Hopkins as Benedict and Jonathan Pryce as Francis, is very humanizing (not initially for Benedict, but his character gets there)—and not just because of the glimpse it provides into Francis’s life prior to the cloth, but also, in part, because of little nods it gives to their interests beyond the church, like Francis’s love of soccer and tango dancing, and Benedict’s piano playing and Fanta drinking. And because it shows their personal fallibility, their regret over past misdeeds.
It should be noted that the meeting of the two men at the papal summer residence of Castel Gandolfo prior to Benedict’s resignation is invented, as are many of their lengthy dialogues, which are nonetheless inspired by speeches, letters, and other writings of theirs, brought into conversation with one another by playwright and screenwriter Anthony McCarten.