SPOTIFY PLAYLIST: January 2026 by Art & Theology: Almost every month I compile thirty faith-inspired songs on Spotify—roughly two hours of listening—to showcase just a sampling of the well-crafted, spiritually nourishing music that is out there. Though this is several days late, here are some songs to kick off the new calendar year.
+++
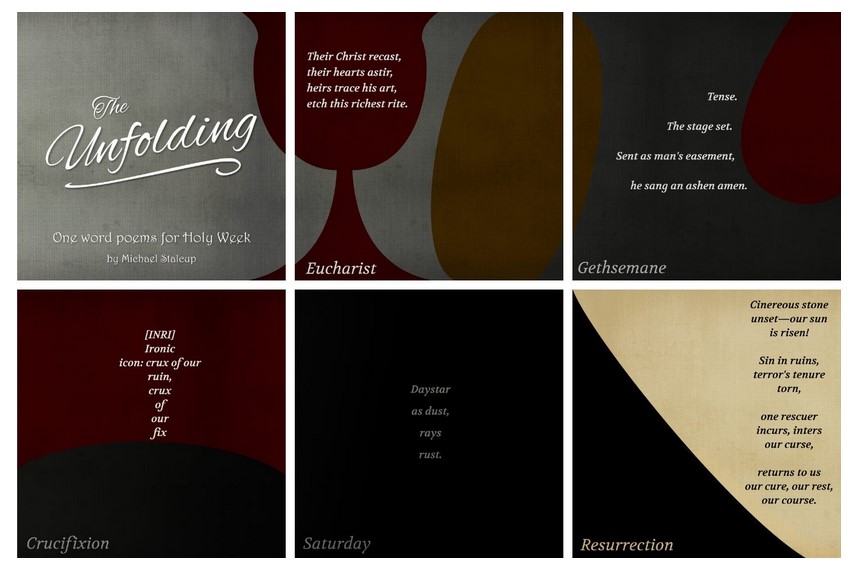
NEW ALBUM + OTHER RESOURCES: Matthew: Gospel Collection by The Soil and The Seed Project: Directed by Seth Thomas Crissman, an educator, musician, and pastor in the Mennonite Church, The Soil and The Seed Project is “a community-supported ministry of the church working for spiritual renewal—in individuals, families, and communities—through beautiful, creative resources that help us together turn towards Jesus in the ordinary moments of life.” I always look forward to their releases, the latest of which is a thirty-song “folk opera,” as they call it, based on the Gospel of Matthew, accompanied by seven commissioned linocut prints by Bethany Tobin (free for church use), seven poems by Michael Stalcup, and twenty-five “little liturgies.”
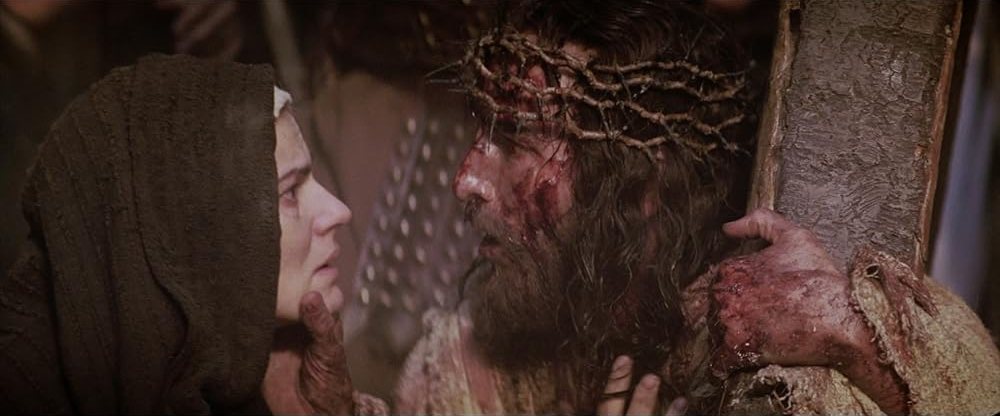
The beautiful opening track, cowritten and performed by Spectator Bird (“Won’t you tell me a story that’s true . . .”), is followed by a range of narrative-based songs (on the Dreams of Joseph, the Temptation in the Wilderness, the Calming of the Storm, the Transfiguration, the Entry into Jerusalem, the Last Supper, the Resurrection, etc.); settings of the Beatitudes, the Lord’s Prayer, and other teachings from the Sermon on the Mount, as well as cherished sayings about the greatest commandment and Jesus’s easy yoke; songs on parables such as the foolish builder, the sower, the lost sheep; and more. There are far fewer songs about Christ’s passion than I would have expected, but that may be because there’s a relative dearth in music that engages the other parts of the Gospel, or because they anticipate overlap with forthcoming Gospel Collection albums on Mark, Luke, and John. I love what they present here.

>> RELEASE CONCERT: On Sunday, January 18, 2026, at 3 p.m. at First Presbyterian Church in Harrisonburg, Virginia, The Soil and The Seed Project are going to perform the entire album from start to finish, with a full band and almost all the contributing artists. Admission is free, but they ask that you consider donating some toiletry items for the local food pantry; there will be a collection box on-site. Find more info at https://www.thesoilandtheseedproject.org/matthew#release-concert.
+++
END-OF-YEAR READING STATS: My Year in Books 2025 (Goodreads): I read 138 books last year, mostly poetry. Exactly half were written by women—I’ve been more intentional about seeking out female authors, ever since someone challenged me on that. I hadn’t realized how disproportionately I was reading male authors, especially for theology. Nothing wrong with men!—but in the interest of closing the gender gap in my personal reading habits so that I can benefit from a wider swath of voices and support women writers, I commit to reading at least as many women as men each year.

(The book covers in this graphic are randomly generated by Goodreads from my list of read books.)
I’ve mentioned several of my favorite recent reads on the blog already (e,g., A Whole Life in Twelve Movies, An Axe for the Frozen Sea, Picturing the Apocalypse), but let me mention a few more. I wish I had time to write thoughtful reviews. I’m obliged to mention that if you make a purchase from any of the following links, I earn a small commission from Amazon.
Five-star single-author poetry collections:
- Mothers of Ireland by Julie Kane
- A Metaphorical God by Kimberly Johnson
- Magic City Gospel by Ashley M. Jones
- Still Pilgrim by Angela Alaimo O’Donnell
Other select books I rated five stars:
- Motherhood: A Confession by Natalie Carnes: This one’s hard to describe, but here’s the publisher’s attempt: “What if Augustine’s Confessions had been written not by a man, but by a mother? How might her tales of desire, temptation, and transformation differ from his? In this memoir, Natalie Carnes describes giving birth to a daughter and beginning a story of conversion strikingly unlike Augustine’s―even as his journey becomes a surprising companion to her own.” Despite my not being a mother, this book, which is also about embodiedness, and by a theologian I’ve met at conferences on multiple occasions, really captivated me. Thank you to a reader who purchased it for me from my wish list!
- I really love the newish Fullness of Time series from InterVarsity Press, edited by Esau McCaulley, which celebrates the riches of the church year in seven short little volumes. It starts with Advent: The Season of Hope by Tish Harrison Warren and Christmas: The Season of Life and Light by Emily Hunter McGowan. As someone who didn’t grow up observing the liturgical calendar but who now does and gets asked about it by Christians for whom it’s unfamiliar, I find these explainers to be a helpful resource as well as personally enriching, and I look forward to reading more.
- Bruegel: The Complete Works: This monster of a book from the art publisher Taschen, which comes in a carrier case, was a present from my husband. It’s beautifully produced, with full-color reproductions, foldouts, essays, and cataloging info. Pieter Bruegel (the Elder), a sixteenth-century Flemish artist, is known for his detailed, densely populated (sometimes a hundred-plus figures!) paintings of biblical narratives and peasant scenes, many of which were copied by his son, Pieter Bruegel the Younger. I give the text four stars but an overall five stars merely for the quality of the images (especially the inclusion of high-resolution details, which are generally not accessible online) and the value of having an authoritative catalog of all the artist’s authenticated works.
Goodreads is a social cataloging website for book lovers. I use it mainly to keep track of the books I’ve read and the ones I want to read. You can also tag books, a feature I use to group by topic or genre, though I’m not entirely consistent with the labeling. I’m a volunteer Goodreads Librarian, meaning I can edit book details and create new book records. Follow me on Goodreads.
+++
Victoria’s Book Wish List: If you would like to support Art & Theology, buying me a book from my Amazon wish list is one tangible way to do that. (Only those with a US Amazon account can do this, I believe.) The books I read influence the content I write and the artists I feature. I keep this link up-to-date year-round, and it lives permanently on this site’s Donate page (where there’s also a link to give financially through PayPal). I only include books that relate to the objectives of this blog. Thank you to those who have gifted me with surprise shipments throughout this past year! My husband says my eyes light up the brightest when I’m receiving a new book. I think it’s because I delight so much in growing my mind and spirit through wisdom and beauty.
Sometimes people ask me how I decide which books to buy versus which to get from the library. On his Astonishing Things Substack, Wes Vander Lugt shares the criteria he uses—and mine are largely the same. He writes:
- Is it a book from a favorite writer that I will want to digest slowly, re-read, and cherish having in my home? Buy it.
- Is it a book that piques my interest but the quality of writing and value of the content is relatively unknown? Get it from the library.
- Is it a novel from a trusted author that I may not be able to finish in a month and/or will most likely want to re-read or at least revisit for inspiration and reflection? Buy it.
- Is it a novel that I can reasonably finish in a month without feeling rushed? Get it from the library, along with the audiobook format if available.
- Is it a book by a friend? Buy it!
- Is it a book by a writer who feels like a friend, and none of the local libraries have a copy after a reasonable time following the release? Buy it.
- Is it a book I would really love to own but my buy-it list is too long? Get it from the library first, and if it strikes a deep chord and the book budget is not maxed out, buy it.
I do get many books from the Linthicum Public Library right down the road from my house here in Maryland, which I usually visit at least once a week. I’m grateful for the service they provide, and for their partnership with Marina Interlibrary Loan, through which I can request books from other libraries in the state. I also regularly borrow movies from the library. However, books that I will take a long time to read, will reference again and again, or would want to lend to a friend—or that simply are not available through the library system in my area but that I desperately want to read and are reasonably priced—those are the kinds I’m likely to add to my wish list or purchase myself.
+++
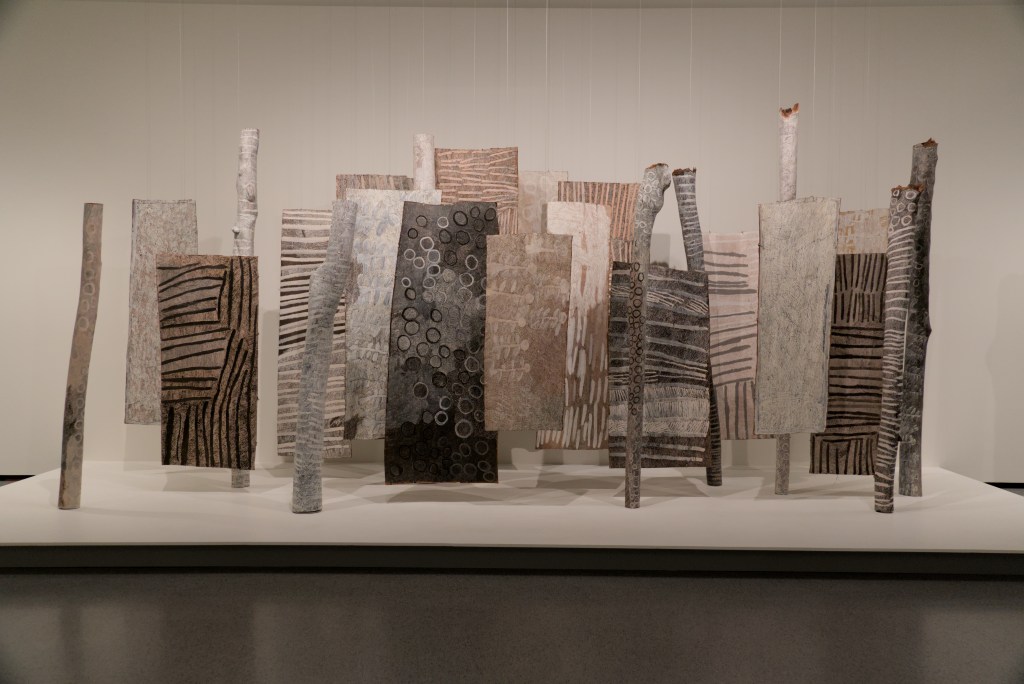
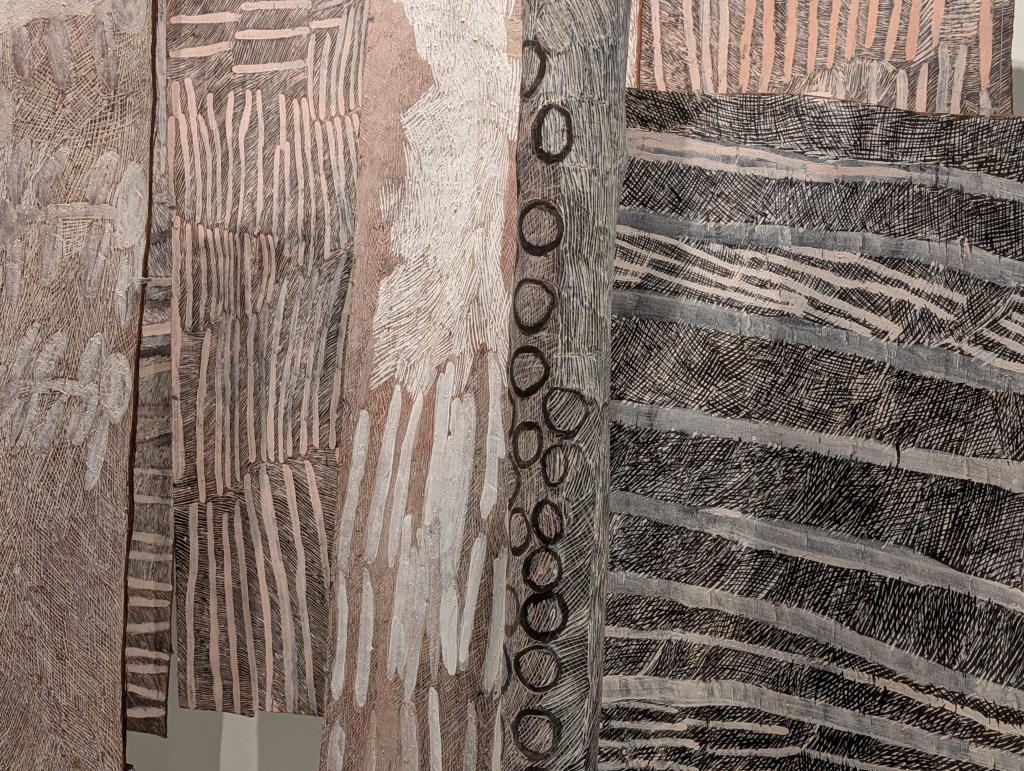
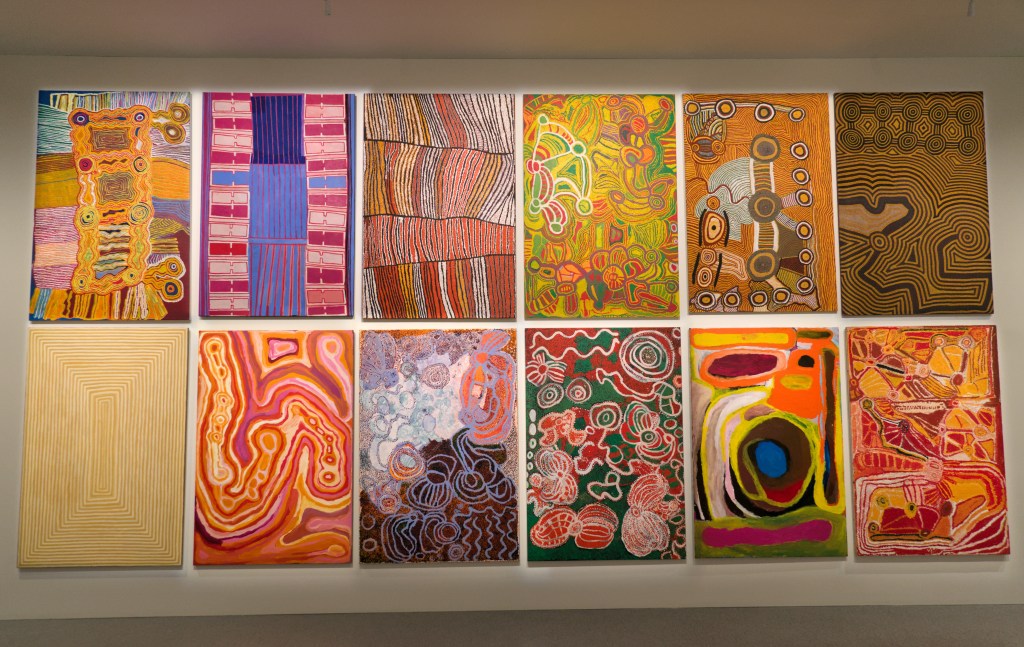
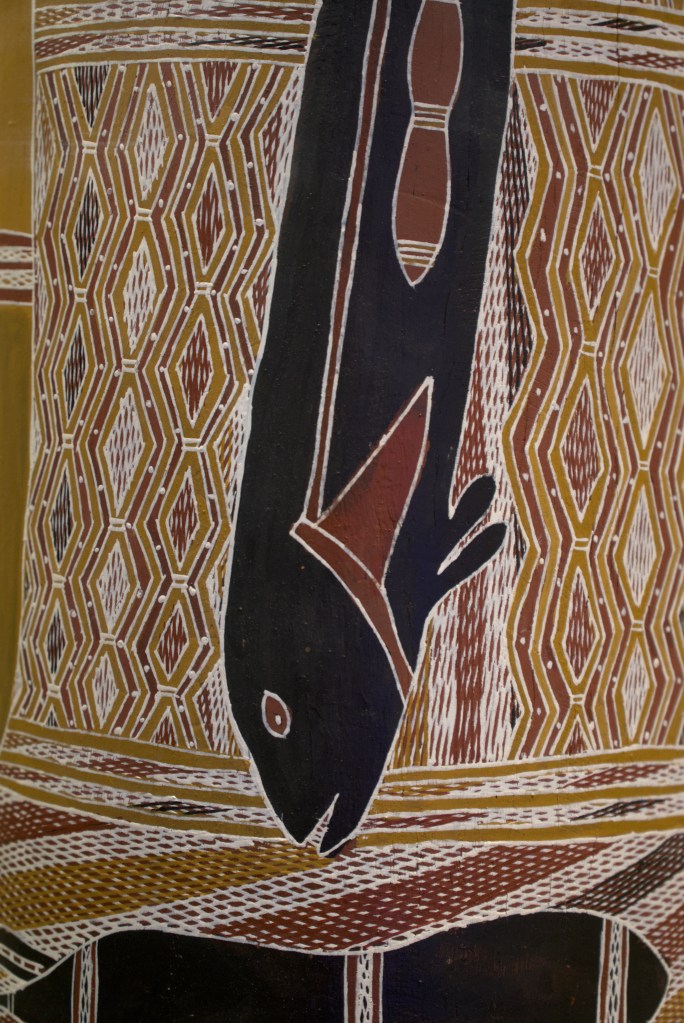
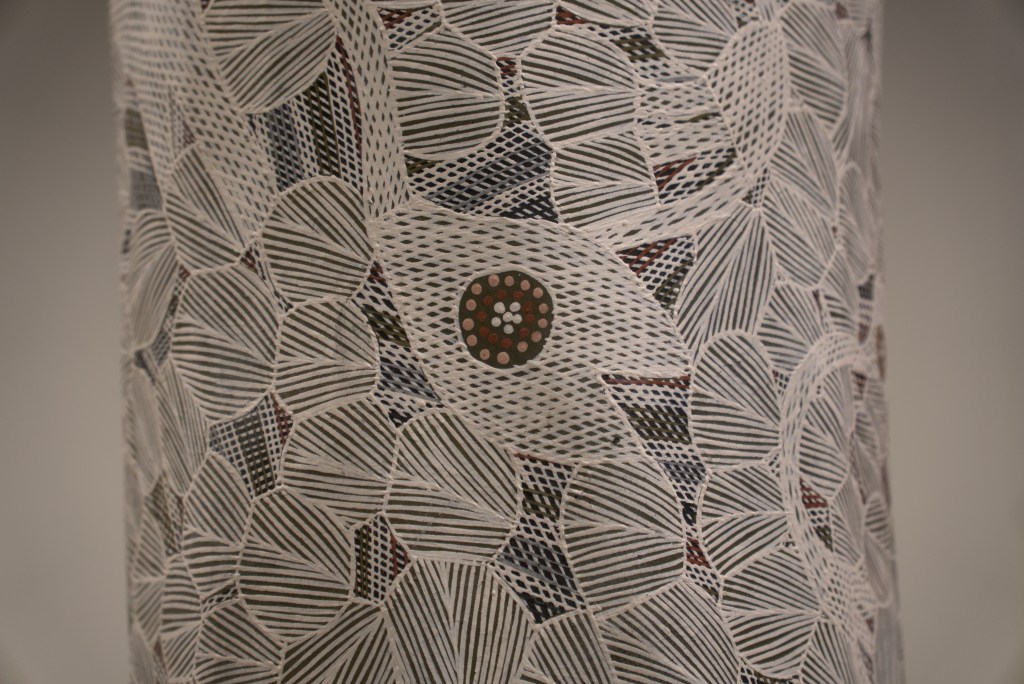
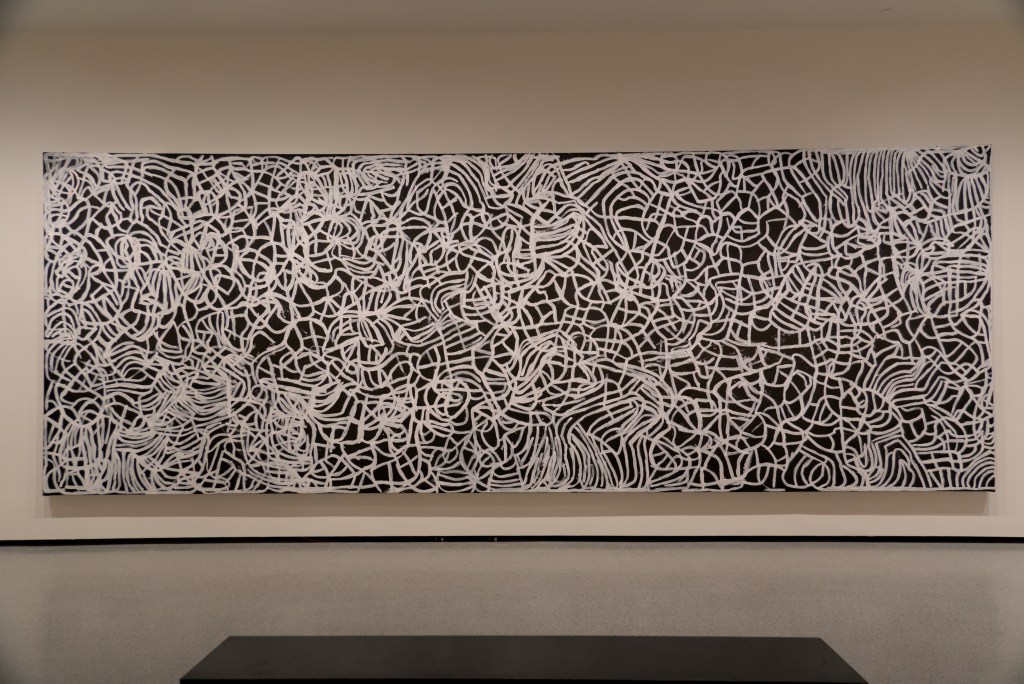
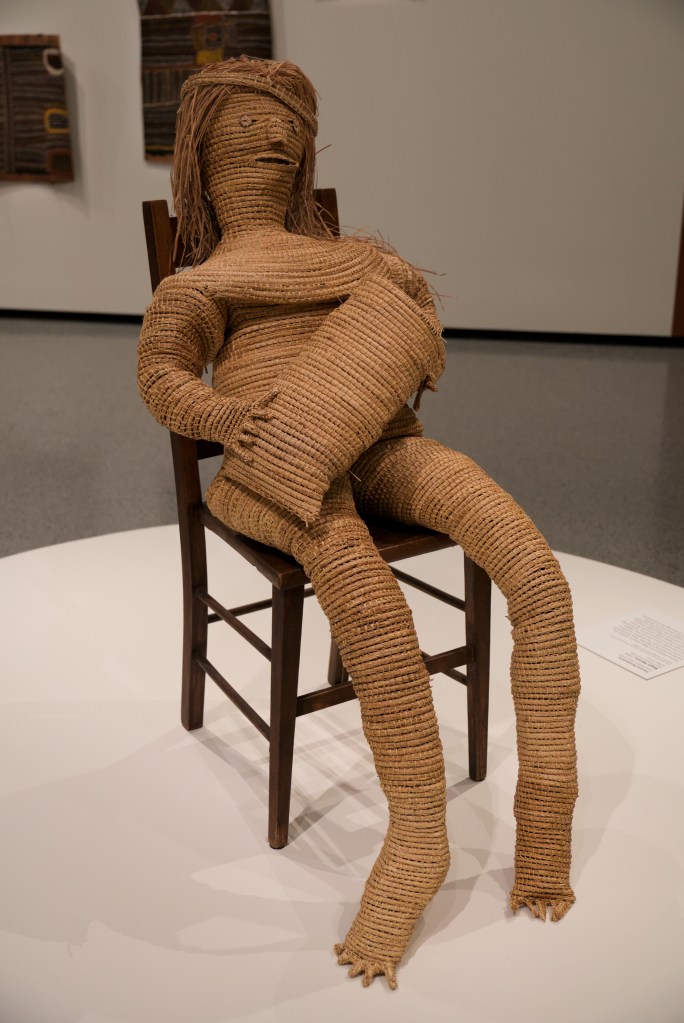
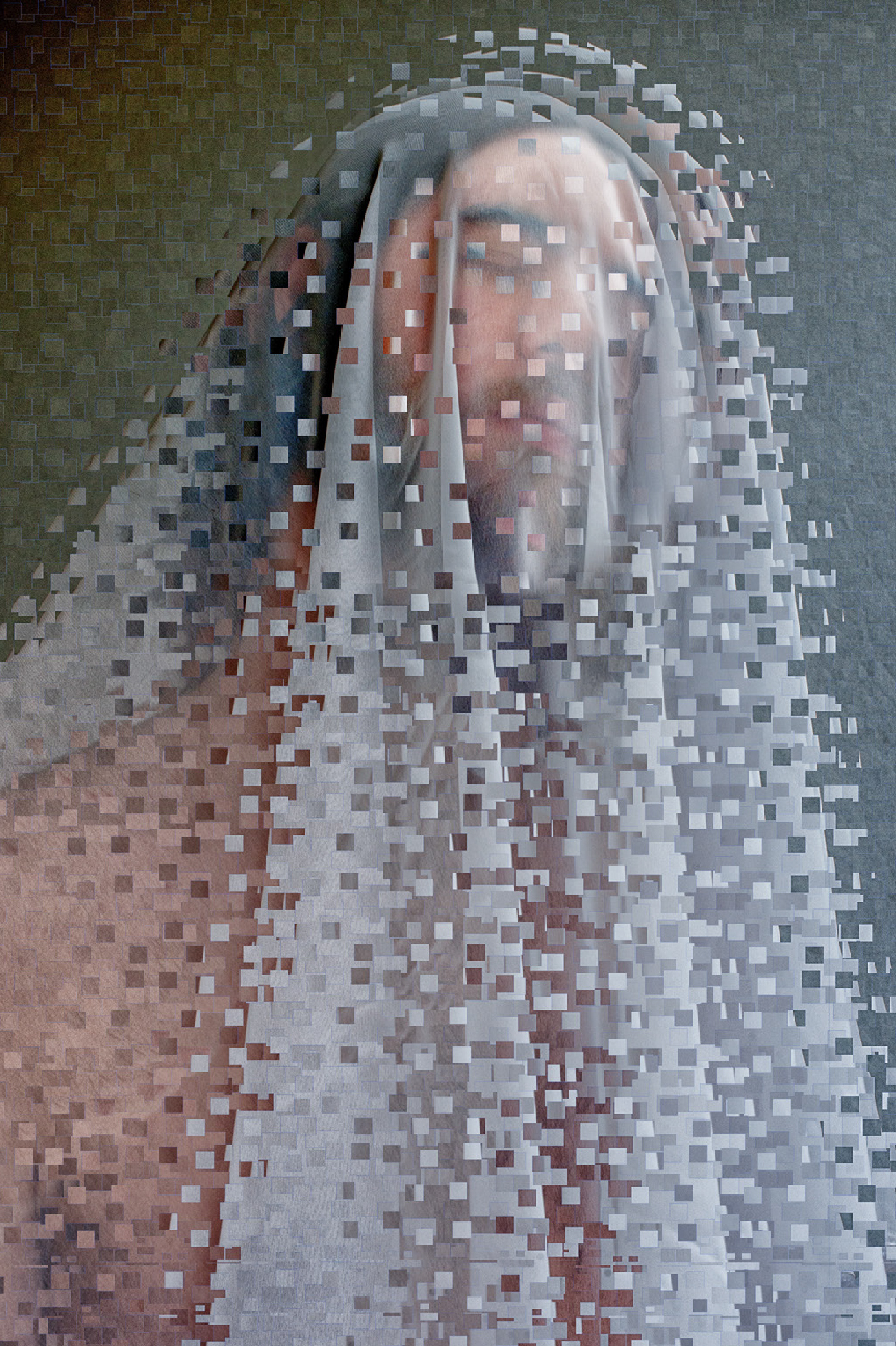
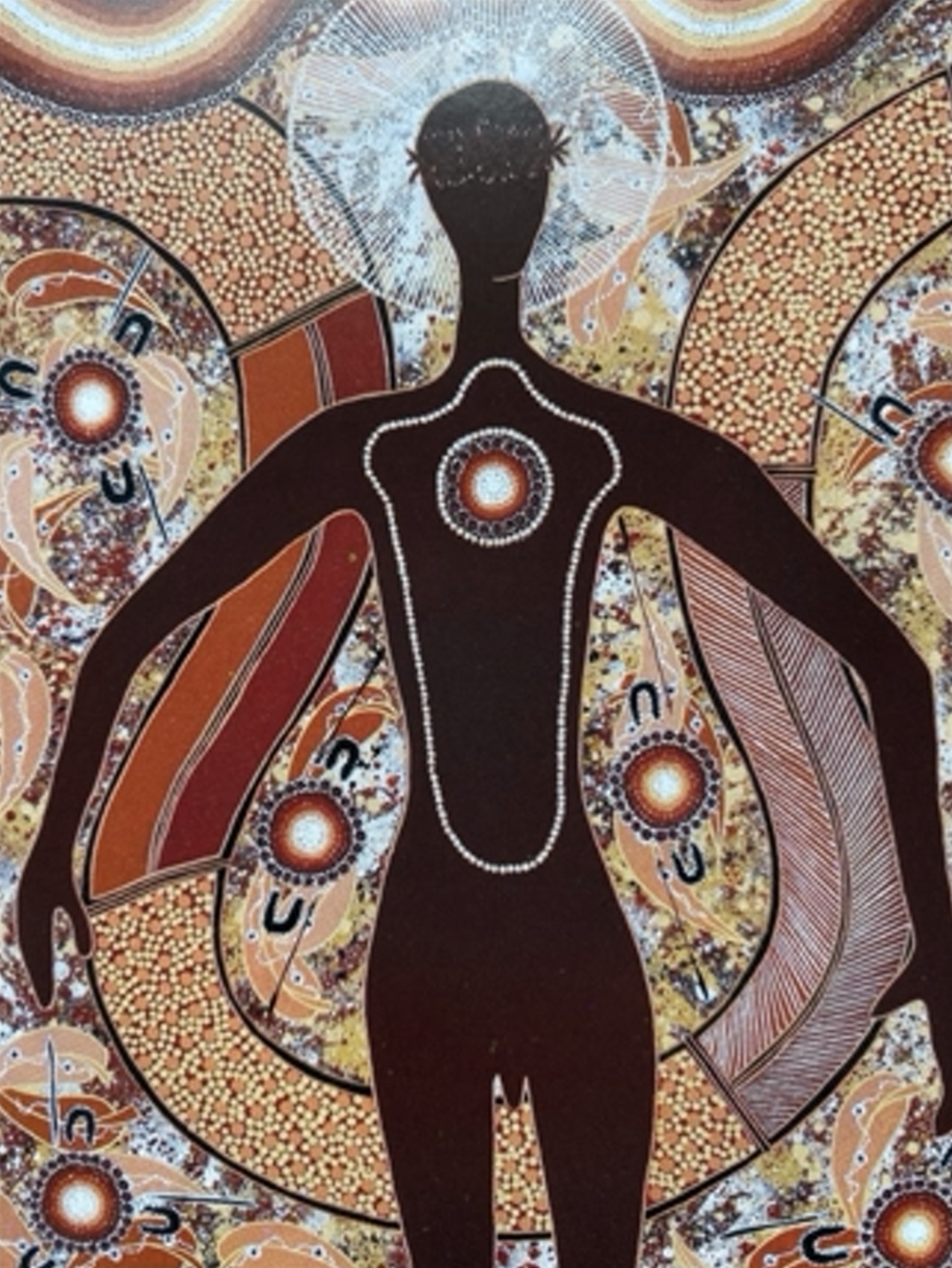
EXHIBITION: The Stars We Do Not See: Australian Indigenous Art, November 15, 2025–March 1, 2026, National Gallery of Art, Washington, DC: I saw this show last month, curated by Myles Russell-Cook from the collection of the National Gallery of Victoria in Melbourne, and it was fantastic. I recommend the free guided tour, especially if Aboriginal art is new to you. “Don’t miss this once-in-a-lifetime exhibition of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander art—the largest ever shown in North America. Australian Indigenous art is a visual thread connecting more than 250 nations across 65,000 years. Explore its breadth and brilliance through nearly 200 works from the late 1800s to today. You’ll find ochre paintings made on bark, maps of the Central and Western deserts (so-called ‘dot paintings’), groundbreaking works in neon, video, and photography, and more. And you’ll meet iconic artists who maintain and reinvigorate Ancestral traditions—revealing the rich, living history of creativity behind the world’s longest continuous culture.”
Here are some of the photos I took:
The title of the exhibition comes from the late artist Gulumbu Yunupiŋu, known affectionately as “Star Lady.” She developed “a signature style characterized by dense networks of crosses unified by fields of dots. Each cross represents a star and all that is visible within the known universe, while the dots in between symbolize everything that remains unknown.” See images 3 and 4 in the slideshow above.
After its run at the National Gallery in Washington, The Stars We Do Not See will be traveling to the Denver Art Museum in Colorado, the Portland Art Museum in Oregon, and the Peabody Essex Museum in Massachusetts.