I came across the following strange image in a book on Christian art at the British Museum, where it appears without any explanation other than that it is part of a group of popular religious prints with Spanish texts that were made in Europe for export to the Spanish-speaking South American market.
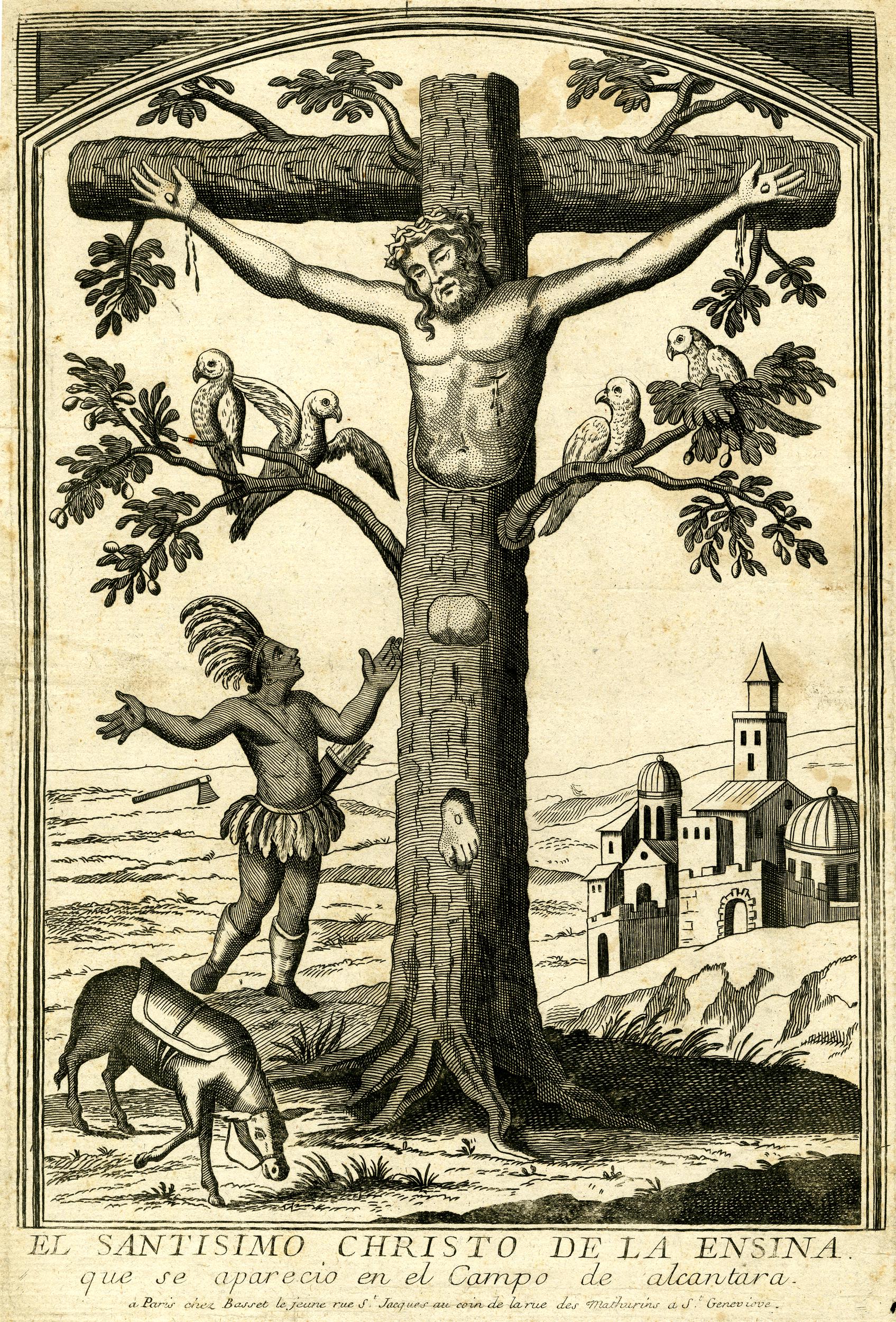

I was intrigued! I had seen art images before where Jesus is crucified on a living tree, his body sometimes melding into the trunk and branches. The motif of the cross as tree of life connects the beginning and the end of time, Eden and the eschaton, placing Christ’s act of self-giving at the crux and communicating its generative impact. But in this particular etching published in Paris, who is the Indigenous man at the base? The caption suggests that the image illustrates a miraculous appearance of Christ (or at least his form) in Latin America—so what’s the story behind it?
The answer is found in the Histórica relación del reyno de Chile (Historical Account of the Kingdom of Chile), a book by the Chilean Jesuit chronicler Alonso de Ovalle (1601–1651), published in Rome in 1646. Ovalle was serving in Rome as procurator for his order and wanted to teach Europeans about his homeland. He was glad to relate a supernatural occurrence, from just a decade prior, of Christ manifesting himself in nature, the subject of chapter 23, titled “En que se da fin a esta materia y se trata el prodigioso árbol que en forma de crucifixo nació en na de las montañas de Chile” (In which this subject is concluded and the prodigious tree that grew in the form of a crucifix in one of the mountains of Chile is discussed).
In 1636, Ovalle writes, an “Indian” in the valley of Limache near Valparaiso in Chile—he would have been Mapuche, though the artist of the Paris print shows him as a Tupi man of Brazil—went to cut down some trees for construction purposes. After striking an ax blow to one, he was astonished to realize that the tree was in the shape of a cross with a man on it. He immediately stopped hacking. The artist shows the ax flying out of the woodcutter’s hands as he throws them up in amazement. The caption reads, “El Santisimo Christo de la Ensina que se aparecio en el Campo de alcantara” (The Most Holy Christ of the Oak that appeared in the Alcántara countryside).
A variation of the legend, according to the blog El Señor de Renca, El Señor de los Milagros by Alejandro Caggiano, says the Mapuche woodcutter was blind, and that when he first struck the tree trunk, a few drops of sap got into his eyes, restoring his sight. It’s then that he saw Christ’s image.
Ovalle does not say whether the man converted to Christianity, but regardless, Ovalle considered the appearance of Christ’s form in the native plant life of Chile as a blessing and an encouragement—Christ taking root in the Americas. He says it should cause the reader to “admire the divine wisdom of our God and his most high providence in the means and motives that he has given us even in natural and insensible things for the confirmation of our faith and the increase of the piety and devotion of his faithful.”
Word spread of the miraculous tree, and pilgrims flocked to see it. Soon, as Orvalle recounts, a noblewoman had the tree uprooted and built a church nearby to house it, placing it behind the altar. That’s the building in the right background of the Paris print.
Sometime after Ovalle’s publication, the Jesuits relocated the tree to Renca, San Luis, in Argentina, just a few miles from Chile’s capital, and veneration continued. A fire destroyed most of the tree in 1729, but its charred remains were incorporated into a new wooden crucifix that is still in Renca. “The Lord of Renca, as the crucifix is now known, is a firm part of the regional religious folklore,” writes Georg T. A. Krizmanics, “and in a song called ‘Zamba del Señor de Renca,’ devoted parishioners and pilgrims cheerfully haunt the Mapuche soul by chanting ‘Christ, you were born Araucanian.’”
The Paris print in the collection of the British Museum is not the first artistic depiction of Christ of the Oak; that credit goes to an anonymous engraving published with Ovalle’s 1646 textual account of the miracle. No Indigenous person appears in this initial version—just the gnarled corpus of Christ crucified, embedded in a tree.

The caption reads, Vera effigies cuiusdam arboris quae in hunc modum et figuram crucis et crucifixi inventa est in Regno Chilensi in America, ubi in Valle Limache colitur magna populi devotione ab anno Domini 1634 (“A true image of a certain tree that was found in this manner in the shape of a cross and a crucifix in the Kingdom of Chile in America, where it has been venerated in the Valle Limache with great devotion by the people since the year 1634”).
Here are some other, later examples of the subject, which attained popularity in Spain.
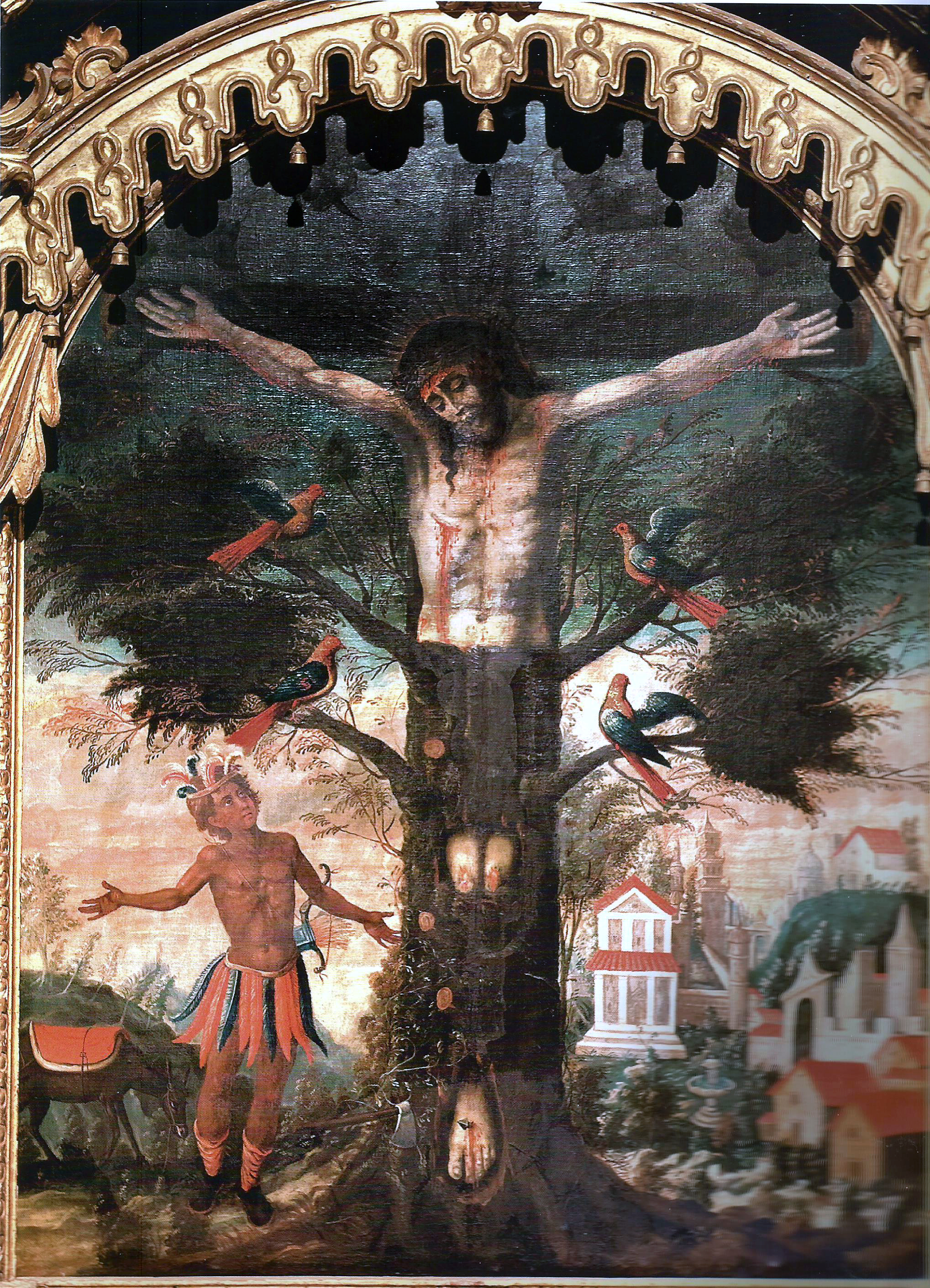


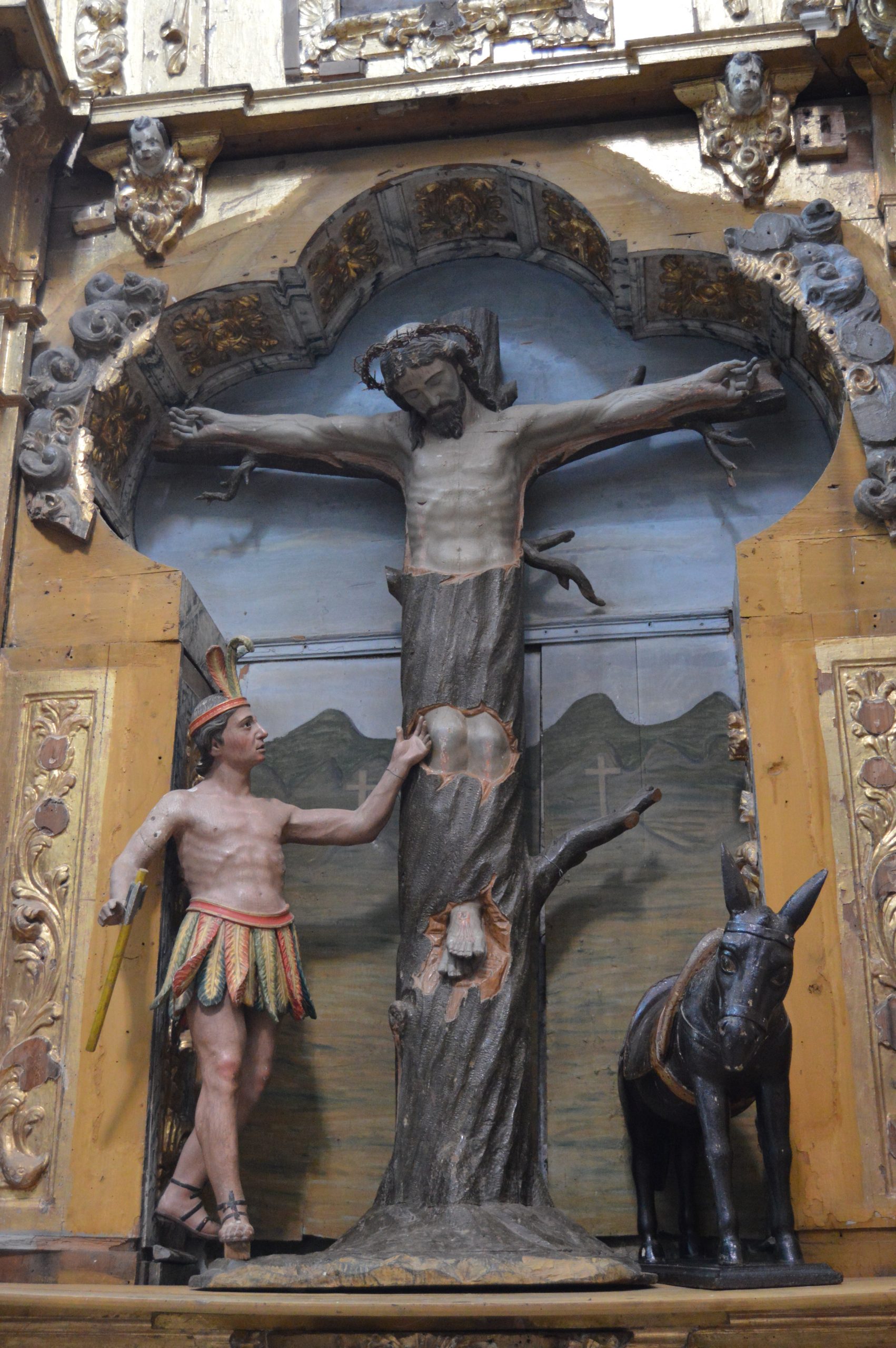
I’m delighted by the parrots perching on the branches! The tree of crucifixion was a site of both death and life. Christ endured its agony so that we, like those birds that are so at home, could find welcome and rest.

One late eighteenth-century painting of Christ of the Oak shows, opposite the woodcutter, a kneeling woman in a black robe. The inscription identifies her as Doña Josefa Posadas. It looks to me like she is holding up a milagro (literally “miracle”), also known as an ex-voto, a small tinplate charm shaped like a body part that is or was in need of healing. Historically in many Hispano-Catholic communities, milagros are pinned to crosses and wooden statues of Christ and the saints, or are hung with ribbons from altars and shrines, to petition the Divine for a cure from a physical ailment or to offer thanks for healing received. Given the shape of Doña Josefa’s milagro, she likely suffered from a heart condition.
Or, it’s possible that it’s not the literal organ that’s referred to in what she holds, but rather the heart as the center of the emotions, will, understanding, and soul, which she offers to Christ.
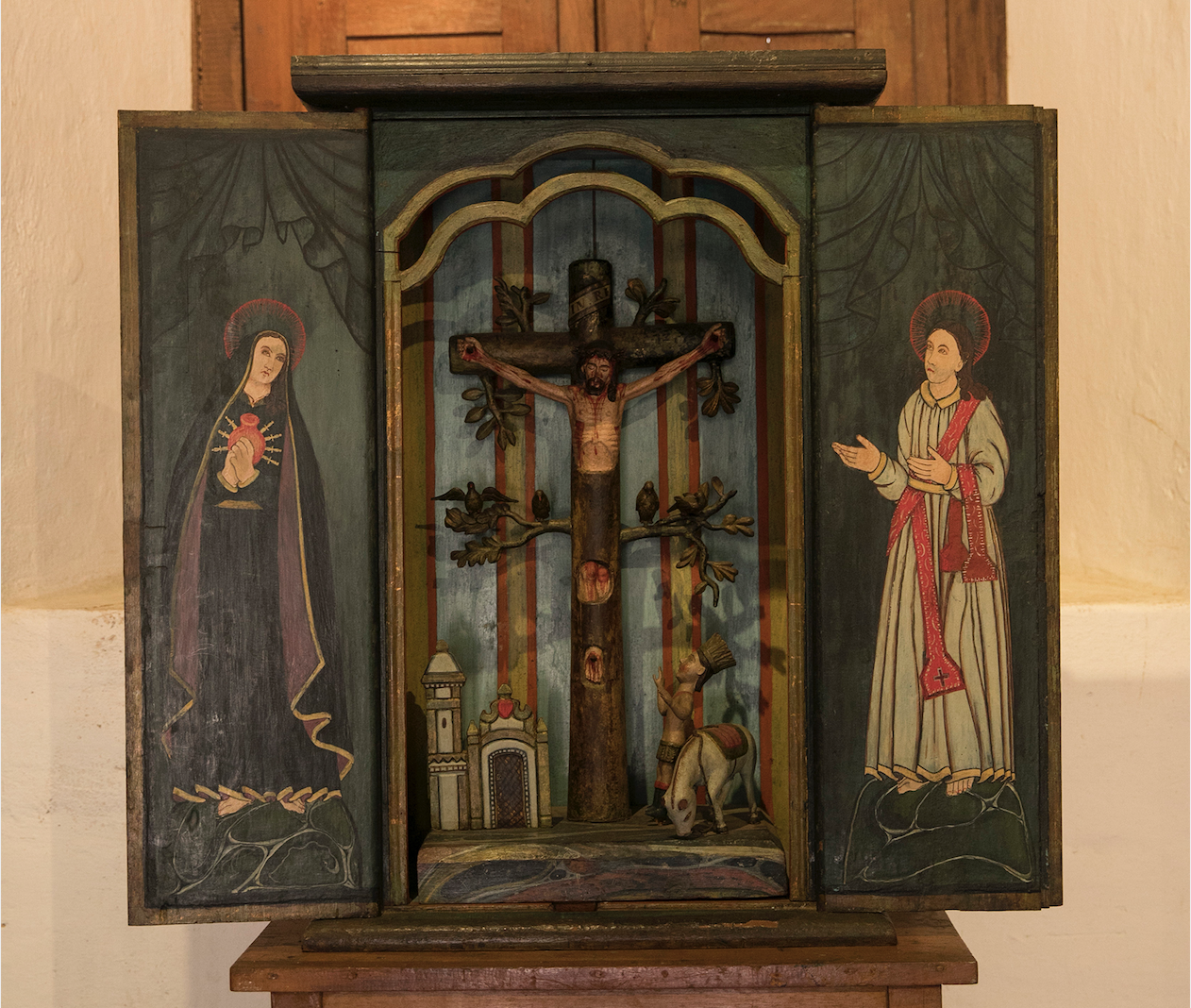



This last example is interesting: in a revision of characters, it shows a Muslim (right) and a Jew whose leg shackles are falling off at the sight of Christ. The painting seems to be an aspirational extension of the Limache legend—a prayer that Christ would reveal himself not only to Indigenous populations but also to those of other religious backgrounds.
I share these images not to affirm or disaffirm the appearance of Christ of the Oak, and not to comment on the colonizing undertones of such images or the cult that sprung up around them, but instead merely to inform you of an iconography that I found curious and compelling and wanted to find out more about. So now if you ever come across an image of Christ crucified on a tree with his bloody knees poking through the bark and an Indigenous, ax-wielding man reacting with surprise, you’ll know a bit about its context!
FURTHER READING
Francisco Javier Pizarro Gómez, “Extremadura en el viaje iconográfico del Cristo de la Encina entre Europa y América” (Extremadura in the iconographic journey of the Christ of the Oak between Europe and America), Quiroga no. 12 (July–December 2017): 72–83.